Yellow Armyworm Life Cycle Guide
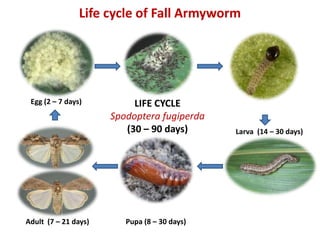
The Yellow Armyworm, also known as Spodoptera exigua, is a significant pest in various agricultural crops worldwide, causing substantial economic losses. Understanding the life cycle of the Yellow Armyworm is crucial for effective management and control strategies. The life cycle of the Yellow Armyworm consists of four stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult.
Introduction to the Yellow Armyworm Life Cycle

The Yellow Armyworm life cycle is complex and influenced by various environmental factors, such as temperature, humidity, and food availability. The female Yellow Armyworm moth can lay up to 1,000 eggs on the underside of leaves or on other surfaces, which hatch into larvae after 2-3 days. The larvae are the most destructive stage, feeding on a wide range of crops, including corn, cotton, and vegetables. The larval stage lasts around 10-14 days, during which the larvae molt several times as they grow.
Egg Stage
The egg stage is the first stage of the Yellow Armyworm life cycle. Female moths lay their eggs in clusters, usually on the underside of leaves or on other surfaces. The eggs are spherical, white, and approximately 0.5 mm in diameter. The egg stage lasts around 2-3 days, during which the eggs are susceptible to predators, parasites, and environmental factors. Temperature and humidity play a crucial role in the egg stage, with optimal conditions ranging from 20-30°C and 60-80% relative humidity.
| Egg Stage Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Egg diameter | 0.5 mm |
| Egg color | White |
| Egg stage duration | 2-3 days |

Larval Stage
The larval stage is the most destructive stage of the Yellow Armyworm life cycle. The larvae are greenish-yellow with a distinctive white stripe running along their back. The larval stage consists of six instars, during which the larvae molt several times as they grow. The larvae feed on a wide range of crops, causing significant damage. Food availability and temperature are critical factors influencing the larval stage, with optimal conditions ranging from 20-30°C and adequate food supply.
Pupal Stage
The pupal stage is the transitional stage between the larval and adult stages. The pupae are usually found in the soil or in protected areas, such as under debris or in vegetation. The pupal stage lasts around 7-10 days, during which the pupae are susceptible to predators, parasites, and environmental factors. Soil moisture and temperature play a crucial role in the pupal stage, with optimal conditions ranging from 20-30°C and 60-80% relative humidity.
| Pupal Stage Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Pupal duration | 7-10 days |
| Pupal location | Soil or protected areas |
| Pupal susceptibility | Predators, parasites, and environmental factors |
Adult Stage
The adult stage is the final stage of the Yellow Armyworm life cycle. The adult moths are brownish-gray with a distinctive white stripe running along their forewings. The adult moths are nocturnal and are attracted to light sources. The adult stage is responsible for reproduction, with female moths laying eggs on suitable hosts. Mating and oviposition are critical factors influencing the adult stage, with optimal conditions ranging from 20-30°C and adequate food supply.
What are the optimal conditions for the Yellow Armyworm life cycle?
+The optimal conditions for the Yellow Armyworm life cycle include temperatures ranging from 20-30°C, relative humidity ranging from 60-80%, and adequate food supply.
What is the most destructive stage of the Yellow Armyworm life cycle?
+The larval stage is the most destructive stage of the Yellow Armyworm life cycle, as the larvae cause significant damage to crops.
In conclusion, understanding the Yellow Armyworm life cycle is essential for effective management and control strategies. By recognizing the different stages and their characteristics, farmers and pest management professionals can develop targeted approaches to mitigate the impact of this significant pest. Integrated pest management strategies, including crop rotation, biological control, and chemical control, can be employed to manage the Yellow Armyworm population and reduce economic losses.
Future Implications and Management Strategies

The Yellow Armyworm is a highly adaptable and resilient pest, and its management requires a comprehensive approach. Future implications of the Yellow Armyworm infestation include the potential for increased resistance to pesticides, the spread of the pest to new areas, and the impact on food security. To address these challenges, research and development of new management strategies, including genetic engineering and biological control, are essential. Additionally, extension services and farmer education programs can play a critical role in promoting integrated pest management practices and reducing the reliance on chemical pesticides.
Ultimately, a comprehensive understanding of the Yellow Armyworm life cycle and its management is critical for reducing the economic and environmental impacts of this significant pest. By working together, farmers, researchers, and pest management professionals can develop effective and sustainable management strategies to mitigate the effects of the Yellow Armyworm and ensure food security for future generations.