When Is 1330 In Standard Time? Time Zone Guide

Understanding time zones and their conversions can be complex, especially when dealing with military time or 24-hour clock formats. The time 1330, in standard time, refers to 1:30 PM. This conversion is straightforward when you understand the basics of the 24-hour clock system, where the day starts at 0000 hours (12:00 AM) and ends at 2359 hours (11:59 PM). To convert 1330 to standard time, you simply break down the numbers: the first two digits (13) represent the hour in 24-hour format, which corresponds to 1:00 PM, and the last two digits (30) represent the minutes.
Time Zone Guide

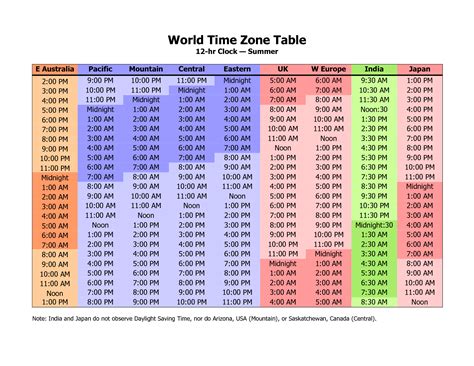
A time zone is a region on Earth that follows a uniform standard time, usually based on the mean solar time at a specific meridian. The world is divided into 24 time zones, each representing a one-hour difference from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). UTC is the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time. It is used to coordinate times across the globe, especially in international communications, transportation, and business. For instance, when it is 1330 UTC, it would be 8:30 AM Eastern Standard Time (EST) in the United States, assuming EST is UTC-5 hours during standard time.
Understanding Time Zones and Their Offsets
To determine what time 1330 is in a specific time zone, you need to know the offset of that time zone from UTC. For example, New York is in the Eastern Time Zone (ET), which is UTC-5 during standard time and UTC-4 during daylight saving time. Los Angeles is in the Pacific Time Zone (PT), which is UTC-8 during standard time and UTC-7 during daylight saving time. If it is 1330 UTC, you would subtract the time zone offset to find the local time. So, for New York (UTC-5), it would be 1330 - 5 hours = 0830 or 8:30 AM, and for Los Angeles (UTC-8), it would be 1330 - 8 hours = 0630 or 6:30 AM.
| Time Zone | UTC Offset (Standard Time) | Local Time for 1330 UTC |
|---|---|---|
| New York (Eastern Time) | -5 hours | 0830 (8:30 AM) |
| Los Angeles (Pacific Time) | -8 hours | 0630 (6:30 AM) |
| London (Greenwich Mean Time) | 0 hours | 1330 (1:30 PM) |
| Sydney (Australian Eastern Time) | +11 hours | 0040 (Next Day, 12:40 AM) |
Daylight Saving Time (DST) Considerations
Daylight Saving Time is the practice of temporarily advancing clocks during the summer months by one hour so that people can make the most of the sunlight during their waking hours. The start and end dates of DST vary by country and sometimes even by region within a country. In the United States, for example, DST typically begins on the second Sunday in March and ends on the first Sunday in November. When converting times, it’s essential to consider whether the region is currently observing standard time or DST, as this will affect the time difference.
Calculating Time Differences with DST
When calculating the time difference between two locations, one must account for DST if it applies. For instance, during standard time, New York is UTC-5, but during DST, it becomes UTC-4. This means that if it’s 1330 UTC during DST, New York would be 1330 - 4 hours = 0930 or 9:30 AM, instead of 8:30 AM as it would be during standard time. Always verify the current time observance (standard or DST) for accurate time conversions.
The time 1330 in standard time, being 1:30 PM, is a straightforward conversion. However, when dealing with different time zones and the potential for DST, conversions can become more complex. Understanding these nuances is essential for seamless international communication and coordination.
How do I convert 1330 to standard time in different time zones?
+To convert 1330 (1:30 PM in 24-hour format) to standard time in different zones, you need to know the UTC offset of the zone. For example, if the zone is UTC-5 (like New York during standard time), you subtract 5 hours from 1330, resulting in 0830 or 8:30 AM. Always consider whether the location is observing standard time or DST, as this affects the offset.
What is the impact of Daylight Saving Time on time zone conversions?
+Daylight Saving Time (DST) changes the local time by one hour, typically advancing it. This means the UTC offset for a region observing DST will be different from its standard time offset. For accurate conversions, it’s crucial to know whether a location is currently on standard time or DST and adjust the UTC offset accordingly.