What Were Us Carriers In Ww2? Key Roles Explained

The United States carriers played a pivotal role in World War II, serving as the backbone of the US Navy's air power in the Pacific Theater. These aircraft carriers, also known as flattops, were floating airbases that enabled the US to project air power across the vast distances of the Pacific Ocean. During the war, the US carriers were instrumental in several key battles and campaigns, including the Battle of Midway, the Battle of the Philippine Sea, and the island-hopping campaign.
Introduction to US Carriers in WW2
The US Navy had a total of 24 aircraft carriers during World War II, with the first being the USS Langley (CV-1), commissioned in 1922. However, it was the later classes of carriers, such as the Yorktown-class and the Essex-class, that formed the core of the US carrier fleet during the war. These carriers were designed to carry a large air group, consisting of fighters, dive bombers, and torpedo bombers, which provided a potent striking force against enemy ships and installations.
Types of US Carriers in WW2
There were several types of US carriers that played important roles during World War II. These included:
- Fleet Carriers: These were the largest and most capable carriers, designed to carry a full air group and operate with the fleet. Examples include the USS Enterprise (CV-6) and the USS Yorktown (CV-5).
- Light Carriers: These were smaller and more lightly armed than fleet carriers, but still carried a significant air group. Examples include the USS Independence (CVL-22) and the USS Belleau Wood (CVL-24).
- Escort Carriers: These were small, slow carriers designed to provide air support for convoys and amphibious landings. Examples include the USS Long Island (CVE-1) and the USS Guadalcanal (CVE-60).
Each type of carrier had its own unique characteristics and strengths, and they were used in various roles throughout the war.
Key Roles of US Carriers in WW2
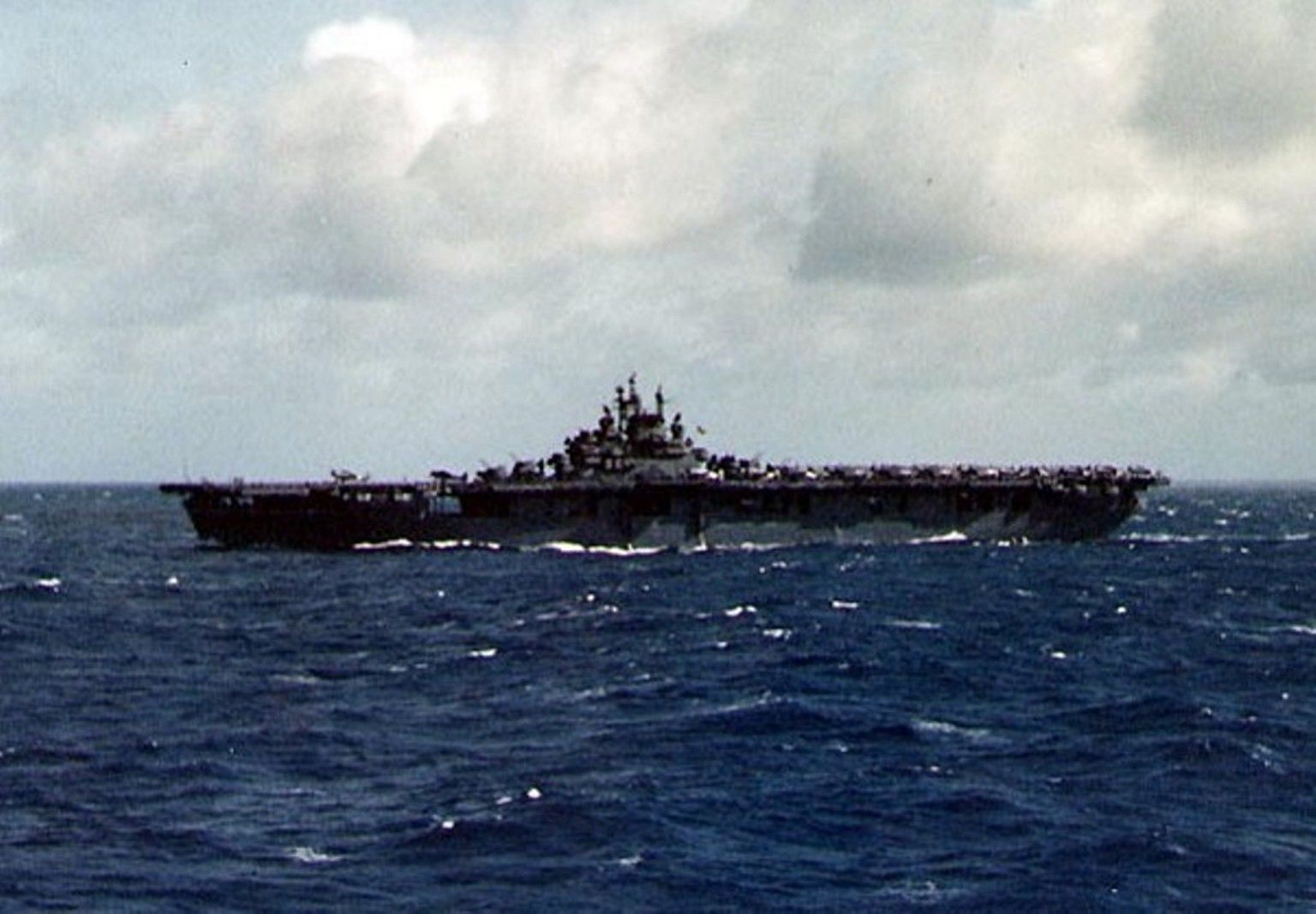

The US carriers played several key roles during World War II, including:
- Air Superiority: US carriers provided air superiority over the battlefield, enabling US forces to control the skies and protect friendly ships and installations from enemy air attack.
- Strike Warfare: US carriers launched strikes against enemy ships and installations, using their air groups to attack and destroy enemy targets.
- Amphibious Warfare: US carriers provided air support for amphibious landings, using their air groups to soften up enemy defenses and provide cover for troops as they landed.
- Convoy Escort: US carriers escorted convoys, providing air protection against enemy submarines and aircraft.
These roles were critical to the success of US forces in the Pacific, and the US carriers played a major part in several key battles and campaigns.
Battles and Campaigns
Some of the key battles and campaigns in which US carriers played a major role include:
- Battle of Midway: This battle, fought in June 1942, was a decisive victory for the US, with US carriers sinking four Japanese carriers and turning the tide of the war in the Pacific.
- Battle of the Philippine Sea: This battle, fought in June 1944, was a major air battle in which US carriers launched strikes against Japanese airfields and sank several Japanese carriers.
- Island-Hopping Campaign: US carriers played a key role in the island-hopping campaign, providing air support for amphibious landings and launching strikes against enemy installations.
These battles and campaigns were critical to the ultimate defeat of Japan, and the US carriers played a major part in the Allied victory.
| Carrier Class | Number of Carriers | Commissioned |
|---|---|---|
| Yorktown-class | 3 | 1937-1940 |
| Essex-class | 24 | 1943-1945 |
| Independence-class | 9 | 1943-1944 |
| Casablanca-class | 50 | 1943-1944 |

Technical Specifications of US Carriers in WW2

The technical specifications of US carriers in WW2 varied depending on the class and type of carrier. However, some common characteristics included:
- Length: 820-900 feet (250-274 meters)
- Beam: 93-108 feet (28-33 meters)
- Draft: 24-28 feet (7-8 meters)
- Displacement: 20,000-30,000 tons
- Speed: 30-33 knots (56-61 kilometers per hour)
- Aircraft Capacity: 50-100 aircraft
These technical specifications gave US carriers the capability to operate a large air group and provide a potent striking force against enemy ships and installations.
Performance Analysis
The performance of US carriers in WW2 was impressive, with several carriers earning numerous awards and commendations for their service. Some notable examples include:
- USS Enterprise (CV-6): Earned 20 battle stars for its service in WW2, including the Battle of Midway and the Battle of the Philippine Sea.
- USS Yorktown (CV-5): Earned 3 battle stars for its service in WW2, including the Battle of Midway.
- USS Essex (CV-9): Earned 13 battle stars for its service in WW2, including the Battle of the Philippine Sea and the island-hopping campaign.
These carriers and their air groups played a major part in the Allied victory in WW2, and their performance was critical to the success of US forces in the Pacific.
What was the main role of US carriers in WW2?
+The main role of US carriers in WW2 was to provide air superiority, strike warfare, and amphibious warfare capabilities to support US forces in the Pacific. They played a critical role in several key battles and campaigns, including the Battle of Midway and the island-hopping campaign.
How many US carriers were there in WW2?
+There were a total of 24 US carriers during WW2, including fleet carriers, light carriers, and escort carriers. These carriers played a major part in the Allied victory, and several earned numerous awards and commendations for their service.
What were some of the key battles and campaigns in which US carriers played a major role?
+Some of the key battles and campaigns in which US carriers played a major role include the Battle of Midway, the Battle of the Philippine Sea, and the island-hopping campaign. These battles and campaigns were critical to the ultimate defeat of Japan, and the US carriers played a major part in the Allied victory.



