What Made Wwii Us Aircraft Carriers Effective?
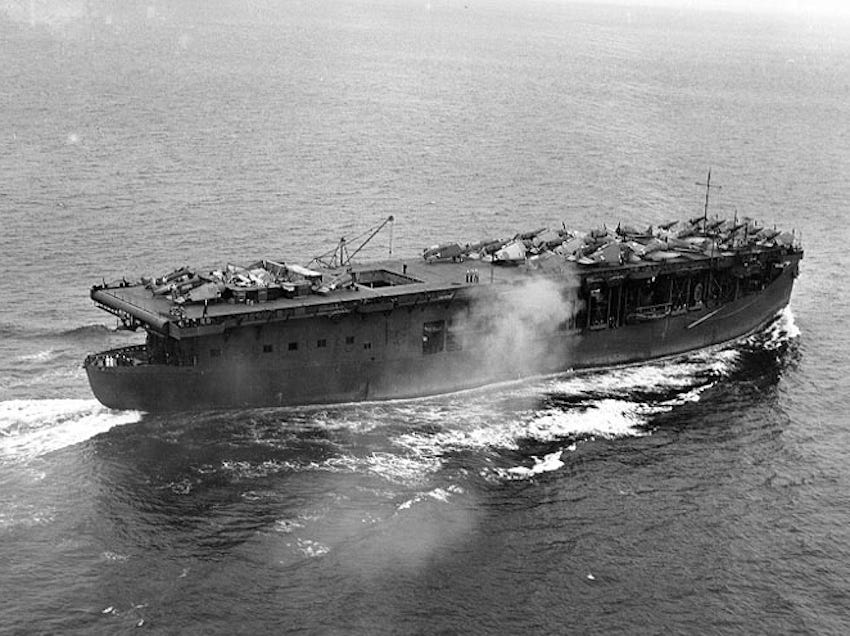

The United States aircraft carriers played a crucial role in World War II, contributing significantly to the Allied victory. Several factors made these carriers effective, including their design, operational tactics, and technological advancements. At the start of the war, the US Navy had a total of seven aircraft carriers, with three more under construction. Despite being outnumbered by the Japanese fleet, the US carriers were able to gain the upper hand due to their superior design and operational capabilities.
Design and Construction

The US aircraft carriers of World War II, such as the Yorktown-class and Essex-class, were designed with several key features that made them highly effective. They had a large flight deck, which allowed for the operation of multiple aircraft simultaneously, and a hangar deck below, which provided storage and maintenance space for the aircraft. The carriers also had a catapult system, which enabled aircraft to take off from the ship with a heavier payload than would have been possible with a traditional runway. Additionally, the carriers were equipped with a recovery system, which included arresting wires and a barrier to prevent aircraft from overshooting the flight deck.
Operational Tactics
The US Navy developed several operational tactics that made their aircraft carriers highly effective. One key tactic was the use of carrier task forces, which consisted of a carrier and its accompanying escorts, such as destroyers and cruisers. These task forces allowed the carriers to operate independently and strike at enemy targets with impunity. The US Navy also developed the concept of carrier air groups, which consisted of a mix of fighter, bomber, and torpedo aircraft. This allowed the carriers to provide a balanced air campaign, with the ability to defend against enemy aircraft, strike at enemy ships, and provide close air support for ground troops.
| Carrier Class | Length | Beam | Displacement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yorktown-class | 809 ft 9 in | 83 ft 3 in | 25,500 tons |
| Essex-class | 872 ft 6 in | 93 ft 2 in | 27,100 tons |

Aircraft and Avionics

The aircraft operated by the US Navy during World War II were highly advanced and played a significant role in the effectiveness of the carriers. The F4F Wildcat and F6F Hellcat were two of the most notable fighter aircraft, with the Hellcat being one of the most successful fighter aircraft of the war. The SBD Dauntless and TBF Avenger were also highly effective, providing the US Navy with a capable dive bomber and torpedo bomber, respectively. The US Navy also made significant advancements in avionics, including the development of radar and radio communication systems, which allowed for more effective coordination and control of aircraft operations.
Logistics and Maintenance
The US Navy’s ability to maintain and repair their aircraft carriers was a critical factor in their effectiveness. The Navy developed a system of forward bases and repair ships, which allowed them to provide maintenance and repair services to the carriers in remote locations. The Navy also developed a logistics system that allowed them to supply the carriers with fuel, ammunition, and spare parts, even in the most remote locations. This allowed the carriers to operate for extended periods without needing to return to a major port for repairs or resupply.
- Forward bases: provided maintenance and repair services to the carriers in remote locations
- Repair ships: provided repair services to the carriers at sea
- Logistics system: supplied the carriers with fuel, ammunition, and spare parts
What was the primary role of US aircraft carriers in World War II?
+The primary role of US aircraft carriers in World War II was to provide air support for naval operations, including strikes against enemy ships and shore-based targets, as well as defense against enemy aircraft and submarines.
What were some of the key design features of US aircraft carriers during World War II?
+Some of the key design features of US aircraft carriers during World War II included a large flight deck, a hangar deck, a catapult system, and a recovery system. These features allowed the carriers to operate multiple aircraft simultaneously and provided a safe and efficient way to launch and recover aircraft.
In conclusion, the effectiveness of US aircraft carriers during World War II was due to a combination of factors, including their design, operational tactics, technological advancements, and logistical support. The carriers played a crucial role in the Allied victory, providing air support for naval operations and defending against enemy aircraft and submarines. The lessons learned from the operation of these carriers during World War II have had a lasting impact on the development of naval aviation and continue to influence the design and operation of aircraft carriers today.