What Is Selective Service Draft Bill? Registration Guide
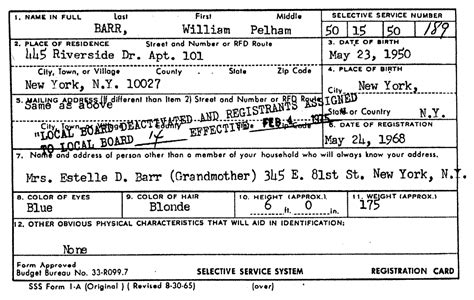
The Selective Service Draft Bill, also known as the Selective Service System, is a federal agency in the United States that maintains information on those potentially subject to military conscription. The system was established by the Selective Draft Act of 1917 and has been modified several times since then. The primary purpose of the Selective Service System is to provide a fair and equitable way of selecting individuals for military service in times of national emergency.
History and Purpose of the Selective Service System

The Selective Service System has a long history dating back to World War I. The system was created to ensure that the military had a sufficient number of personnel to fight in the war. The draft, also known as conscription, is the mandatory enrollment of people in a national service, most often a military service. The Selective Service System is responsible for maintaining a list of all male U.S. citizens between the ages of 18 and 25, as well as male immigrants living in the United States, who are eligible for military service.
Registration Requirements
According to the Selective Service System, all male U.S. citizens between the ages of 18 and 25 are required to register with the system. This includes U.S.-born males, male immigrants, and male non-citizens living in the United States. Registration is typically done online or by mail, and it is a simple process that requires basic information such as name, date of birth, and address. Females are not currently required to register with the Selective Service System, although there have been discussions about making registration mandatory for both males and females.
The following individuals are required to register with the Selective Service System:
- Male U.S. citizens between the ages of 18 and 25
- Male immigrants living in the United States
- Male non-citizens living in the United States
Individuals who are exempt from registration include:
- Females
- Non-citizens who are not living in the United States
- Members of the active military
- Conscientious objectors
Registration Process

The registration process is straightforward and can be completed online or by mail. To register online, individuals can visit the Selective Service System website and fill out the registration form. The form requires basic information such as name, date of birth, and address. Once the form is submitted, the individual will receive a registration acknowledgement letter in the mail.
To register by mail, individuals can download and complete the registration form from the Selective Service System website, or they can pick up a form at a local post office. The completed form should be mailed to the Selective Service System, and the individual will receive a registration acknowledgement letter in the mail.
| Registration Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Online Registration | Visit the Selective Service System website and fill out the registration form |
| Mail Registration | Download and complete the registration form, or pick up a form at a local post office and mail it to the Selective Service System |

Consequences of Not Registering
Failure to register with the Selective Service System can have serious consequences. Individuals who do not register may be ineligible for federal student loans, grants, and other forms of federal assistance. They may also be barred from federal employment and may face fines and imprisonment.
Future of the Selective Service System
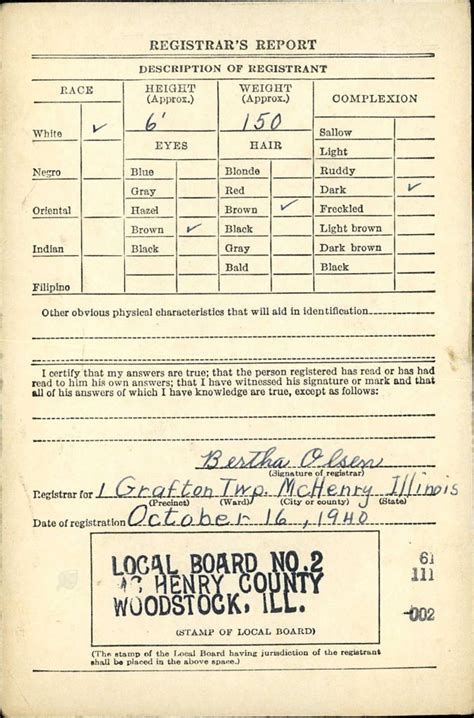
The future of the Selective Service System is uncertain, and there have been discussions about whether the system is still necessary. Some argue that the system is outdated and that it is no longer necessary to have a draft. Others argue that the system is essential for national security and that it provides a fair and equitable way of selecting individuals for military service.
In recent years, there have been efforts to make registration mandatory for both males and females. In 2019, the National Commission on Military, National, and Public Service released a report that recommended making registration mandatory for both males and females. The report argued that registering both males and females would provide a more diverse pool of potential recruits and would help to ensure that the military has the personnel it needs to defend the country.
What is the purpose of the Selective Service System?
+The purpose of the Selective Service System is to provide a fair and equitable way of selecting individuals for military service in times of national emergency.
Who is required to register with the Selective Service System?
+Male U.S. citizens between the ages of 18 and 25, male immigrants living in the United States, and male non-citizens living in the United States are required to register with the Selective Service System.
What are the consequences of not registering with the Selective Service System?
+Failure to register with the Selective Service System can result in ineligibility for federal student loans, grants, and other forms of federal assistance. Individuals who do not register may also be barred from federal employment and may face fines and imprisonment.


