What Causes World War? Expert Insights
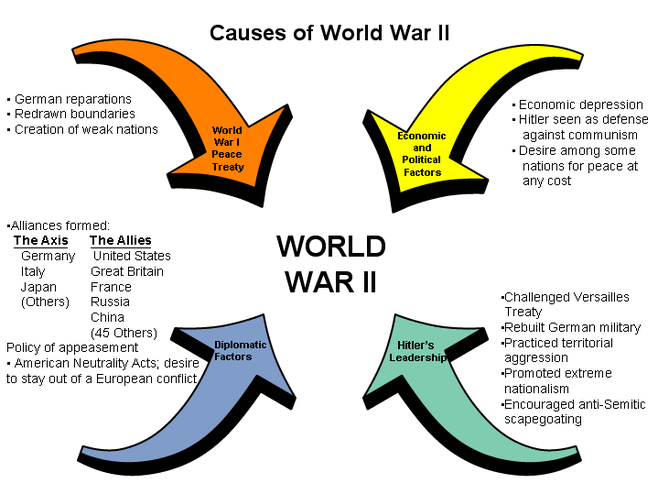
The question of what causes world war is a complex and multifaceted one, with various factors contributing to the outbreak of global conflict. To understand the root causes of world war, it is essential to examine the historical context, political climate, and social dynamics that precede such events. Geopolitical tensions, economic instability, and ideological differences are often cited as key factors that can escalate into full-blown conflict. Additionally, the realist theory of international relations suggests that the pursuit of power and security by nation-states can lead to an arms race, alliances, and ultimately, war.
In the lead-up to World War I, for instance, the complex system of alliances between European powers, including the Triple Entente and the Triple Alliance, created an environment in which a small conflict could quickly escalate into a larger war. The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand in 1914 served as a catalyst, triggering a chain reaction of events that eventually led to the outbreak of war. Similarly, in the years preceding World War II, the aggressive expansion of Nazi Germany, fascist Italy, and imperial Japan, combined with the policy of appeasement by other major powers, created an environment in which war became increasingly likely.
Historical Context and Causes of World War

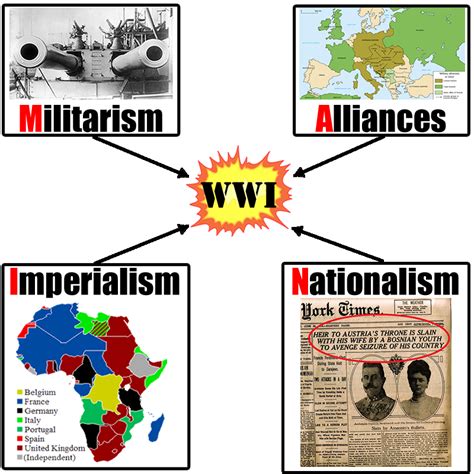
A thorough examination of historical events reveals that the causes of world war are often deeply rooted in the political, economic, and social context of the time. Nationalism, imperialism, and militarism were significant contributing factors to the outbreak of both World War I and World War II. The rise of nationalist sentiment in various countries, coupled with the pursuit of imperial ambitions and the glorification of military power, created an atmosphere in which war was seen as a viable means of achieving national objectives.
The interwar period between World War I and World War II is also noteworthy, as it was marked by widespread economic instability, including the Great Depression, which had a profound impact on international relations. The economic crisis led to increased protectionism, trade wars, and a decline in international cooperation, further exacerbating tensions between nations. Furthermore, the appeasement policy pursued by Britain and France towards Nazi Germany, which involved giving in to some of Germany's demands in the hope of avoiding war, ultimately emboldened Hitler's aggressive expansionism.
Role of International Relations Theories
International relations theories, such as realism, liberalism, and constructivism, offer valuable insights into the causes of world war. Realist theorists argue that the international system is anarchic, meaning there is no central authority to enforce laws or maintain order, and that states must rely on self-help to ensure their security. This can lead to an arms race and an increased likelihood of conflict. Liberal theorists, on the other hand, emphasize the importance of international institutions, diplomacy, and economic interdependence in promoting peace and cooperation. Constructivist theorists focus on the role of ideas, identities, and norms in shaping state behavior and international relations.
The following table illustrates the main international relations theories and their views on the causes of war:
| Theory | View on Causes of War |
|---|---|
| Realism | Anarchy of the international system, pursuit of power and security by states |
| Liberalism | Failure of international institutions, lack of economic interdependence, and insufficient diplomacy |
| Constructivism | Clash of ideas, identities, and norms between states, and the construction of security threats |

Prevention of Future Wars
Given the devastating consequences of world war, it is essential to consider strategies for preventing future conflicts. Diplomacy, international cooperation, and the promotion of peace and security are critical components of any effort to prevent war. The establishment of international institutions, such as the United Nations, has been instrumental in promoting dialogue, resolving conflicts peacefully, and addressing common global challenges.
Furthermore, economic interdependence can serve as a powerful deterrent to war, as nations that are economically intertwined are less likely to engage in conflict with one another. The European Union, for example, has been successful in promoting peace and stability among its member states through economic integration and cooperation. Additionally, confidence-building measures, such as arms control agreements and military transparency, can help to reduce tensions and prevent the escalation of conflicts.
Role of International Law
International law plays a crucial role in preventing war by establishing clear rules and norms for state behavior. The United Nations Charter, for instance, prohibits the use of force by states except in cases of self-defense or when authorized by the UN Security Council. The Geneva Conventions and their additional protocols also provide a framework for the conduct of war, protecting civilians and prisoners of war from the effects of conflict.
The following list highlights key international laws and treaties that aim to prevent war:
- United Nations Charter
- Geneva Conventions and their additional protocols
- Hague Conventions
- Chemical Weapons Convention
- Biological Weapons Convention
What are the main causes of world war?
+The main causes of world war include geopolitical tensions, economic instability, ideological differences, nationalism, imperialism, and militarism. The complex interplay of these factors can lead to an increased likelihood of conflict.
How can future wars be prevented?
+Future wars can be prevented through diplomacy, international cooperation, the promotion of peace and security, economic interdependence, and the establishment of international institutions. Confidence-building measures, such as arms control agreements and military transparency, can also help to reduce tensions and prevent conflict.



