What Are Life Scientist Tools? Essential Lab Guide
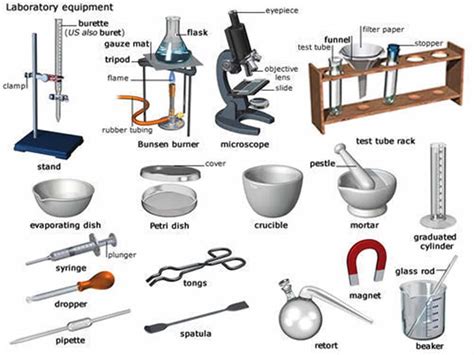
Life scientists rely on a wide range of tools to conduct experiments, collect data, and analyze results. These tools are essential for advancing our understanding of biological systems, developing new treatments, and improving human health. In this guide, we will explore the various life scientist tools that are commonly used in laboratories, their applications, and the benefits they provide. From microscopes and spectrophotometers to PCR machines and next-generation sequencers, we will delve into the world of life science tools and their significance in modern research.
Introduction to Life Scientist Tools

Life scientist tools are specialized instruments designed to facilitate various laboratory tasks, such as sample preparation, data collection, and data analysis. These tools can be broadly categorized into several groups, including microscopy, spectroscopy, molecular biology, and cell culture. Each category comprises a range of tools that serve specific purposes, such as visualizing cells, analyzing biomolecules, or culturing microorganisms. By utilizing these tools, life scientists can gain a deeper understanding of biological systems, identify potential therapeutic targets, and develop innovative treatments.
Microscopy Tools
Microscopy tools are used to visualize and study the morphology of cells, tissues, and microorganisms. The most common microscopy tools include light microscopes, fluorescence microscopes, and electron microscopes. Light microscopes use visible light to illuminate samples, while fluorescence microscopes use fluorescent dyes to highlight specific structures or molecules. Electron microscopes, on the other hand, use a beam of electrons to produce high-resolution images of samples. These tools are essential for understanding cellular structure, identifying biomarkers, and diagnosing diseases.
| Microscopy Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Light Microscope | Uses visible light to illuminate samples |
| Fluorescence Microscope | Uses fluorescent dyes to highlight specific structures or molecules |
| Electron Microscope | Uses a beam of electrons to produce high-resolution images of samples |

Spectroscopy Tools

Spectroscopy tools are used to analyze the interactions between matter and electromagnetic radiation. These tools include UV-Vis spectrophotometers, infrared spectrometers, and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectrometers. UV-Vis spectrophotometers measure the absorption of light by molecules, while infrared spectrometers analyze the vibrational modes of molecules. NMR spectrometers, on the other hand, use magnetic fields to analyze the structure and dynamics of molecules. These tools are essential for understanding biomolecular structure, identifying biomarkers, and developing diagnostic assays.
Molecular Biology Tools
Molecular biology tools are used to manipulate and analyze DNA, RNA, and proteins. The most common molecular biology tools include PCR machines, gel electrophoresis systems, and next-generation sequencers. PCR machines amplify specific DNA sequences, while gel electrophoresis systems separate and analyze DNA, RNA, or protein molecules based on their size and charge. Next-generation sequencers, on the other hand, enable high-throughput sequencing of genomes and transcriptomes. These tools are essential for understanding gene function, identifying genetic variants, and developing personalized therapies.
| Molecular Biology Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| PCR Machine | Amplifies specific DNA sequences |
| Gel Electrophoresis System | Separates and analyzes DNA, RNA, or protein molecules based on their size and charge |
| Next-Generation Sequencer | Enables high-throughput sequencing of genomes and transcriptomes |
Cell Culture Tools

Cell culture tools are used to maintain and manipulate cells in the laboratory. The most common cell culture tools include incubators, microscopes, and cell sorters. Incubators provide a controlled environment for cell growth, while microscopes enable visualization and monitoring of cell morphology. Cell sorters, on the other hand, enable the isolation and purification of specific cell populations. These tools are essential for understanding cellular behavior, developing cell-based therapies, and testing drug efficacy.
Cell Culture Techniques
Cell culture techniques are used to manipulate and analyze cells in the laboratory. The most common cell culture techniques include cell passaging, cell transfection, and cell differentiation. Cell passaging involves the transfer of cells from one culture vessel to another, while cell transfection involves the introduction of foreign DNA into cells. Cell differentiation, on the other hand, involves the induction of cells to adopt specific cell fates. These techniques are essential for understanding cellular development, identifying therapeutic targets, and developing cell-based therapies.
What is the purpose of life scientist tools?
+The purpose of life scientist tools is to facilitate various laboratory tasks, such as sample preparation, data collection, and data analysis, to advance our understanding of biological systems and develop innovative treatments.
What are the different types of life scientist tools?
+Life scientist tools can be broadly categorized into several groups, including microscopy, spectroscopy, molecular biology, and cell culture. Each category comprises a range of tools that serve specific purposes, such as visualizing cells, analyzing biomolecules, or culturing microorganisms.
What is the importance of life scientist tools in modern research?
+Life scientist tools are essential for advancing our understanding of biological systems, developing new treatments, and improving human health. They enable researchers to collect and analyze data, identify potential therapeutic targets, and develop innovative therapies.
In conclusion, life scientist tools are essential for advancing our understanding of biological systems and developing innovative treatments. By utilizing these tools, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of cellular behavior, identify potential therapeutic targets, and develop cell-based therapies. The choice of life scientist tool depends on the specific research question, sample type, and desired level of resolution. By selecting the appropriate tool and technique, researchers can optimize their experiments, collect and analyze high-quality data, and make significant contributions to the field of life sciences.



