Specific Heat Of Cu

The specific heat of copper (Cu) is a fundamental physical property that characterizes its ability to absorb and release thermal energy. Copper, with its atomic number 29, is a popular and versatile metal used extensively in various industries, including electrical, construction, and manufacturing. Its specific heat capacity, denoted as c, is crucial for understanding how copper behaves under different thermal conditions.
Introduction to Specific Heat Capacity

Specific heat capacity is defined as the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by one degree Celsius (or Kelvin). It is an intensive property, meaning its value does not depend on the size or amount of the substance. For copper, the specific heat capacity is a critical parameter in designing and optimizing systems where thermal management is essential, such as in electronics, heat exchangers, and thermal storage devices.
Value of Specific Heat of Cu
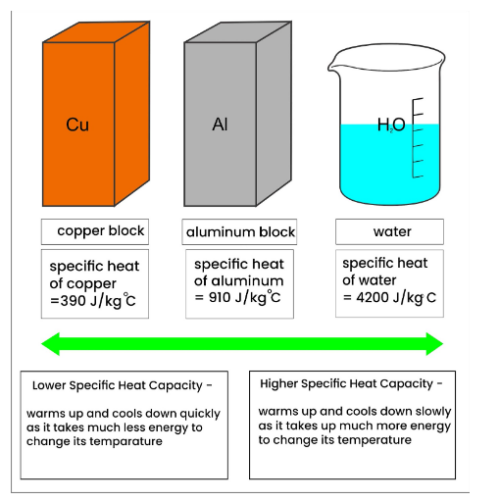
The specific heat capacity of copper is approximately 0.385 J/g·K at room temperature (20°C). This value indicates that 0.385 joules of heat energy are needed to increase the temperature of one gram of copper by one Kelvin. The specific heat of copper is relatively low compared to other metals and materials, which makes it an efficient conductor of heat.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Specific Heat Capacity (c) | 0.385 J/g·K |
| Density | 8.96 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 1085°C |
| Boiling Point | 2562°C |

Factors Influencing Specific Heat of Cu

The specific heat capacity of copper can be influenced by several factors, including temperature, pressure, and the presence of impurities. At higher temperatures, the specific heat of copper increases, which affects its thermal behavior. Additionally, the microstructure and purity of the copper alloy can also impact its specific heat capacity, making it essential to consider these factors in practical applications.
Temperature Dependence
The specific heat capacity of copper is not constant and varies with temperature. At low temperatures, the specific heat of copper decreases, approaching zero as it reaches absolute zero. At elevated temperatures, the specific heat increases due to the increased thermal motion of the atoms. Understanding this temperature dependence is crucial for accurately modeling and predicting the thermal behavior of copper in various applications.
Experimental measurements have shown that the specific heat of copper can be described by the following equation: c = 0.385 + 0.0006T, where T is the temperature in Kelvin. This equation provides a simplified model for estimating the specific heat capacity of copper at different temperatures.
What is the significance of specific heat capacity in thermal design?
+The specific heat capacity is crucial in thermal design as it determines how much heat energy a material can absorb or release. This property is vital for designing efficient heat exchangers, thermal storage systems, and electronic components where heat management is critical.
How does the purity of copper affect its specific heat capacity?
+The purity of copper can influence its specific heat capacity. Impurities can alter the microstructure and lattice vibrations of the copper, potentially affecting its thermal properties. High-purity copper tends to have a more consistent and predictable specific heat capacity.
Applications of Copper’s Specific Heat
The specific heat capacity of copper plays a significant role in various applications, including electronics, construction, and energy storage. In electronics, copper’s high thermal conductivity and relatively low specific heat make it an ideal material for heat sinks and thermal interfaces. In construction, copper is used in plumbing and heating systems due to its excellent thermal properties. Additionally, copper’s specific heat capacity is utilized in thermal energy storage systems, where it helps to efficiently store and release thermal energy.
Thermal energy storage systems, for example, rely on the specific heat capacity of materials like copper to absorb and release heat energy. By understanding and optimizing the specific heat capacity of copper and other materials, these systems can be designed to be more efficient and effective, contributing to advancements in renewable energy and sustainable technologies.
In conclusion, the specific heat capacity of copper is a fundamental property that underpins its applications in thermal management, energy storage, and other fields. Understanding the factors that influence copper’s specific heat, such as temperature and purity, is essential for optimizing its use in various technologies. As research and development continue to advance, the role of copper’s specific heat capacity in innovative applications is likely to grow, contributing to more efficient, sustainable, and high-performance systems across multiple industries.



