Russian Current Time: Know Time Difference Easily
Russia, the world's largest country by land area, spans across eleven time zones, making it a complex task to keep track of the current time. The time difference between Russia and other countries can be quite significant, and understanding this difference is essential for international communication, travel, and business. In this article, we will explore the Russian time zones, their corresponding time differences, and provide an easy way to calculate the current time in Russia.
Russian Time Zones
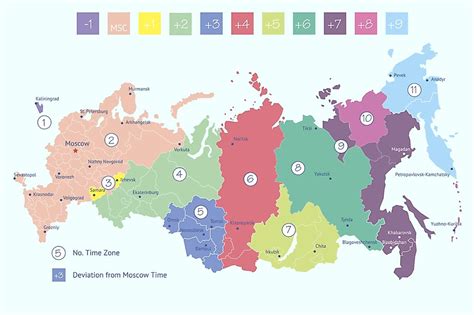
Russia has eleven time zones, each with its own unique offset from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). The time zones are: Kaliningrad Time (UTC+2), Moscow Time (UTC+3), Samara Time (UTC+4), Yekaterinburg Time (UTC+5), Omsk Time (UTC+6), Krasnoyarsk Time (UTC+7), Irkutsk Time (UTC+8), Yakutsk Time (UTC+9), Vladivostok Time (UTC+10), Magadan Time (UTC+11), and Kamchatka Time (UTC+12). Moscow Time is the most widely used time zone in Russia, and it is often considered the country’s standard time zone.
Time Difference Calculation
To calculate the time difference between Russia and another country, you need to know the UTC offset of both locations. For example, if you want to know the time difference between Moscow (UTC+3) and New York (UTC-5), you would subtract the UTC offset of New York from the UTC offset of Moscow: 3 - (-5) = 8. This means that Moscow is 8 hours ahead of New York. UTC offset is the difference in hours between a location’s local time and Coordinated Universal Time (UTC).
| Russian Time Zone | UTC Offset | Example Cities |
|---|---|---|
| Kaliningrad Time | UTC+2 | Kaliningrad, Moscow (during daylight saving time) |
| Moscow Time | UTC+3 | Moscow, St. Petersburg |
| Samara Time | UTC+4 | Samara, Izhevsk |
| Yekaterinburg Time | UTC+5 | Yekaterinburg, Perm |
| Omsk Time | UTC+6 | Omsk, Novosibirsk |
| Krasnoyarsk Time | UTC+7 | Krasnoyarsk, Abakan |
| Irkutsk Time | UTC+8 | Irkutsk, Ulaanbaatar |
| Yakutsk Time | UTC+9 | Yakutsk, Verkhoyansk |
| Vladivostok Time | UTC+10 | Vladivostok, Nakhodka |
| Magadan Time | UTC+11 | Magadan, Anadyr |
| Kamchatka Time | UTC+12 | Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, Klyuchi |

Daylight Saving Time (DST) in Russia

Russia has a complex system of daylight saving time (DST), with some regions observing DST and others not. In 2014, Russia permanently switched to winter time, effectively abolishing DST. However, some regions, such as Kaliningrad, still observe DST. It is essential to check the current DST rules for each region to ensure accurate time calculations.
Regional Time Zones
Russia’s regional time zones are often divided into two categories: European Russia and Asian Russia. European Russia includes time zones such as Moscow Time, Samara Time, and Kaliningrad Time, while Asian Russia includes time zones such as Yekaterinburg Time, Omsk Time, and Vladivostok Time. Understanding these regional time zones is crucial for calculating the time difference between Russia and other countries.
In addition to the regional time zones, Russia also has several autonomous regions with their own unique time zones. For example, the Chukchi Autonomous Okrug is located in the Kamchatka Time zone, while the Sakha Republic is located in the Yakutsk Time zone. These autonomous regions often have their own distinct cultural and economic characteristics, which can affect the way time is perceived and used.
What is the current time in Moscow?
+The current time in Moscow is UTC+3. However, during daylight saving time, Moscow observes UTC+3, but this is not currently in effect. To get the current time in Moscow, you can use an online world clock or a time zone converter tool.
How many time zones does Russia have?
+Russia has 11 time zones, each with its own unique offset from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). These time zones are: Kaliningrad Time, Moscow Time, Samara Time, Yekaterinburg Time, Omsk Time, Krasnoyarsk Time, Irkutsk Time, Yakutsk Time, Vladivostok Time, Magadan Time, and Kamchatka Time.
Does Russia observe daylight saving time?
+Russia permanently switched to winter time in 2014, effectively abolishing daylight saving time (DST). However, some regions, such as Kaliningrad, still observe DST. It is essential to check the current DST rules for each region to ensure accurate time calculations.
In conclusion, understanding the Russian time zones and their corresponding time differences is essential for international communication, travel, and business. By using online tools and resources, you can easily calculate the current time in Russia and stay connected with the country's vast and diverse regions. Whether you are planning a trip to Moscow or conducting business with Russian companies, knowing the time difference will help you navigate the complexities of Russia's time zones and ensure successful interactions.
Future Implications of Russian Time Zones

The Russian time zones have significant implications for the country’s economy, culture, and international relations. As Russia continues to grow and develop, its time zones will play an increasingly important role in shaping the country’s global presence. Trade and commerce will be affected by the time differences between Russia and other countries, with businesses needing to adapt to the unique time zones of each region. Cultural exchange will also be influenced by the time zones, with events and activities needing to be scheduled according to the local time.
Economic Impact of Time Zones
The Russian time zones have a significant impact on the country’s economy, with trade and commerce being affected by the time differences between Russia and other countries. Businesses need to adapt to the unique time zones of each region, taking into account the time differences when scheduling meetings, deliveries, and other activities. The time zones also affect the logistics and transportation industries, with companies needing to plan routes and schedules according to the local time.
In addition to the economic impact, the Russian time zones also have a significant cultural impact. The time zones influence the way people live, work, and interact with each other, with cultural events and activities being scheduled according to the local time. The time zones also affect the education system, with schools and universities needing to adapt to the unique time zones of each region.



