Parts Of An Engine
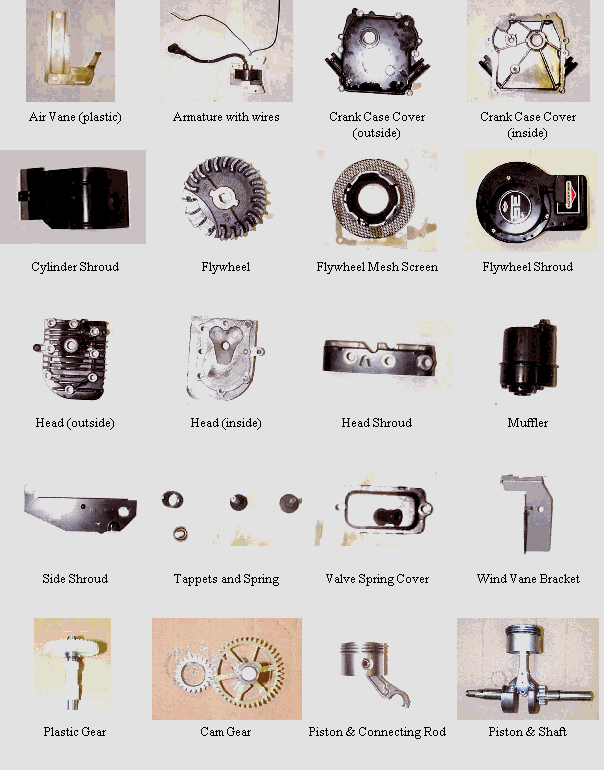
The internal combustion engine is a complex piece of machinery that has been the backbone of the automotive industry for over a century. It is a type of heat engine that generates power by burning fuel, typically gasoline or diesel, inside a combustion chamber within the engine. The engine consists of several major components, each playing a crucial role in the engine's operation. In this article, we will delve into the various parts of an engine, exploring their functions, importance, and interactions.
Major Engine Components

The major components of an engine can be broadly categorized into several groups, including the cylinder block, cylinder head, crankshaft, camshaft, valves, pistons, and connecting rods. Each of these components works in harmony to facilitate the four stages of the combustion process: intake, compression, power, and exhaust.
Cylinder Block and Cylinder Head
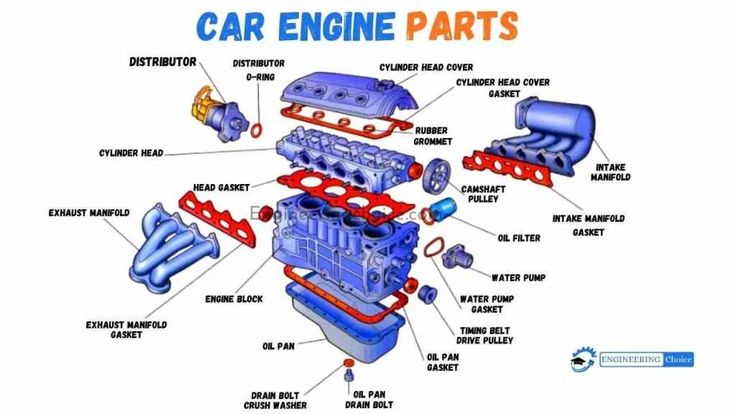
The cylinder block, also known as the engine block, is the main structural component of the engine. It houses the cylinders, which are the chambers where the fuel is burned to produce power. The cylinder head, on the other hand, sits on top of the cylinder block and plays a critical role in the engine’s operation. It contains the valves, spark plugs, and other components that control the flow of air and fuel into the cylinders and the exhaust gases out of the cylinders. The cylinder head is typically made of aluminum or cast iron and is designed to withstand the high temperatures and pressures generated by the combustion process.
Crankshaft and Camshaft
The crankshaft is a long, rod-like component that converts the up-and-down motion of the pistons into rotational energy. It is connected to the pistons via the connecting rods and is responsible for transmitting the power generated by the engine to the transmission. The camshaft, on the other hand, is a rod-like component that operates the valves, controlling the flow of air and fuel into the cylinders and the exhaust gases out of the cylinders. It is typically driven by the crankshaft via a timing belt or chain and is designed to ensure that the valves open and close at the correct time.
Valves and Pistons
The valves are responsible for controlling the flow of air and fuel into the cylinders and the exhaust gases out of the cylinders. They are typically operated by the camshaft and are designed to open and close at the correct time to facilitate the combustion process. The pistons, on the other hand, are the components that move up and down in the cylinders, driven by the explosive force of the combustion process. They are connected to the crankshaft via the connecting rods and play a critical role in converting the energy released by the combustion process into rotational energy.
| Engine Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Cylinder Block | Houses the cylinders and provides the main structural component of the engine |
| Cylinder Head | Contains the valves, spark plugs, and other components that control the flow of air and fuel into the cylinders and the exhaust gases out of the cylinders |
| Crankshaft | Converts the up-and-down motion of the pistons into rotational energy |
| Camshaft | Operates the valves, controlling the flow of air and fuel into the cylinders and the exhaust gases out of the cylinders |
| Valves | Control the flow of air and fuel into the cylinders and the exhaust gases out of the cylinders |
| Pistons | Move up and down in the cylinders, driven by the explosive force of the combustion process |
Engine Performance and Efficiency
The performance and efficiency of an engine are critical factors that determine its suitability for various applications. Engine performance is typically measured in terms of its power output, torque, and speed, while efficiency is measured in terms of its fuel consumption and emissions. The engine’s design and operation play a crucial role in determining its performance and efficiency, with factors such as the compression ratio, camshaft design, and valve timing all having a significant impact.
Compression Ratio and Camshaft Design
The compression ratio is a critical factor that determines the engine’s efficiency and performance. It is defined as the ratio of the cylinder’s volume when the piston is at the bottom of its stroke to the volume when the piston is at the top of its stroke. A higher compression ratio typically results in higher efficiency and performance, but it also increases the risk of engine knock or pinging. The camshaft design also plays a critical role in determining the engine’s performance and efficiency, with factors such as the camshaft’s lift, duration, and timing all having a significant impact.
Valve Timing and Engine Performance
The valve timing is a critical factor that determines the engine’s performance and efficiency. It is defined as the timing of the valves’ opening and closing, with the goal of maximizing the engine’s power output and efficiency. The valve timing is typically controlled by the camshaft and is designed to ensure that the valves open and close at the correct time to facilitate the combustion process.
- Engine performance is typically measured in terms of its power output, torque, and speed
- Efficiency is measured in terms of its fuel consumption and emissions
- The compression ratio is a critical factor that determines the engine's efficiency and performance
- The camshaft design plays a critical role in determining the engine's performance and efficiency
- The valve timing is a critical factor that determines the engine's performance and efficiency
What is the function of the cylinder head in an engine?
+The cylinder head contains the valves, spark plugs, and other components that control the flow of air and fuel into the cylinders and the exhaust gases out of the cylinders. It plays a critical role in the engine’s operation and is responsible for ensuring that the engine runs efficiently and effectively.
How does the compression ratio affect engine performance and efficiency?
+The compression ratio is a critical factor that determines the engine’s efficiency and performance. A higher compression ratio typically results in higher efficiency and performance, but it also increases the risk of engine knock or pinging. The ideal compression ratio will depend on the specific engine design and application, but it is typically in the range of 8:1 to 12:1.
What is the function of the camshaft in an engine?
+The camshaft operates the valves, controlling the flow of air and fuel into the cylinders and the exhaust gases out of the cylinders. It is typically driven by the crankshaft via a timing belt or chain and is designed to ensure that the valves open and close at the correct time to facilitate the combustion process.


