How To Use Stainless Steel Mig Gas? Tips Inside

Stainless steel MIG (GMAW) welding requires a specific set of skills and knowledge to produce high-quality welds. One crucial aspect of this process is the use of shielding gases, which protect the arc and molten metal from atmospheric gases. In this article, we will delve into the world of stainless steel MIG gas, exploring its composition, applications, and tips for optimal use.
Introduction to Stainless Steel MIG Gas
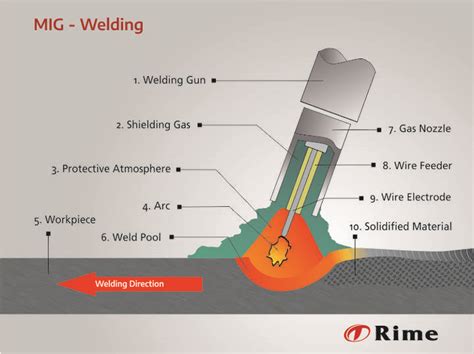
Stainless steel MIG gas is a mixture of gases designed to provide a shielding atmosphere for welding stainless steel alloys. The most common mixture is a combination of argon and carbon dioxide (Ar+CO2) or argon and oxygen (Ar+O2). The specific composition of the gas mixture depends on the type of stainless steel being welded, the desired weld properties, and the welding equipment being used.
Types of Stainless Steel MIG Gas Mixtures
There are several types of stainless steel MIG gas mixtures available, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. Some common mixtures include:
- 75% Argon + 25% CO2: This mixture is commonly used for welding austenitic stainless steels, such as 304 and 316.
- 90% Argon + 10% CO2: This mixture is often used for welding ferritic and martensitic stainless steels, such as 409 and 410.
- 98% Argon + 2% O2: This mixture is sometimes used for welding duplex stainless steels, such as 2205 and 2507.
Tips for Using Stainless Steel MIG Gas

To get the most out of your stainless steel MIG gas, follow these tips:
1. Choose the right gas mixture: Select a gas mixture that is compatible with the type of stainless steel you are welding. Using the wrong gas mixture can result in porosity, lack of fusion, or other weld defects.
2. Use the correct flow rate: The flow rate of the shielding gas should be sufficient to protect the arc and molten metal from atmospheric gases. A flow rate of 20-30 cubic feet per hour (CFH) is typical for most stainless steel MIG welding applications.
3. Maintain a consistent gas flow: Ensure that the gas flow is consistent throughout the welding process. Fluctuations in gas flow can affect the weld quality and cause defects.
4. Use a high-quality gas regulator: A good gas regulator is essential for maintaining a consistent gas flow and pressure. Look for a regulator that is specifically designed for MIG welding and has a high flow rate capacity.
Gas Regulator Settings
The gas regulator settings will depend on the specific welding application and equipment being used. Here are some general guidelines:
| Gas Mixture | Flow Rate (CFH) | Pressure (PSI) |
|---|---|---|
| 75% Ar + 25% CO2 | 20-25 | 15-20 |
| 90% Ar + 10% CO2 | 25-30 | 20-25 |
| 98% Ar + 2% O2 | 20-25 | 15-20 |

Common Challenges and Solutions
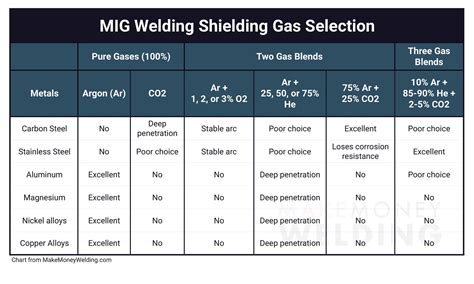
Despite the many advantages of stainless steel MIG gas, there are some common challenges that welders may encounter. Here are some solutions to common problems:
Porosity: Porosity can be caused by insufficient gas flow, high humidity, or contamination. To prevent porosity, ensure that the gas flow is sufficient, the welding area is clean and dry, and the shielding gas is of high quality.
Lack of fusion: Lack of fusion can be caused by insufficient heat input, incorrect gas mixture, or poor joint preparation. To prevent lack of fusion, ensure that the welding parameters are set correctly, the gas mixture is compatible with the stainless steel being welded, and the joint is properly prepared.
Troubleshooting Guide
Here is a troubleshooting guide to help you identify and solve common problems:
- Porosity: Check gas flow, humidity, and contamination.
- Lack of fusion: Check welding parameters, gas mixture, and joint preparation.
- Weld defects: Check gas flow, shielding gas quality, and welding technique.
What is the recommended gas flow rate for stainless steel MIG welding?
+The recommended gas flow rate for stainless steel MIG welding is 20-30 CFH.
What is the difference between argon and carbon dioxide shielding gases?
+Argon is an inert gas that provides a stable shielding atmosphere, while carbon dioxide is an active gas that can affect the weld chemistry and microstructure.