How Low Is F22 Radar Cross Section? Evasion Tactics Revealed
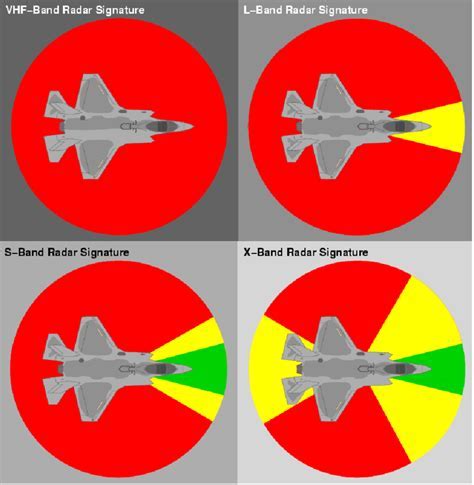
The F-22 Raptor, a fifth-generation stealth fighter jet developed by Lockheed Martin, is renowned for its exceptional radar-evading capabilities. One of the key factors contributing to its stealthiness is its remarkably low radar cross-section (RCS). The RCS of an aircraft is a measure of how much radar energy it reflects back to the radar antenna, and a lower RCS indicates a smaller radar signature, making the aircraft harder to detect.
The exact RCS of the F-22 is classified, but it is widely reported to be less than 0.01 square meters, which is an incredibly low value compared to other fighter jets. For context, the RCS of a typical fourth-generation fighter jet can be around 1-10 square meters, depending on the aircraft's design and materials. The F-22's low RCS is achieved through a combination of design features, including its curved surfaces, serrated edges, and the use of radar-absorbing materials (RAMs) in its construction.
Design Features Contributing to Low RCS
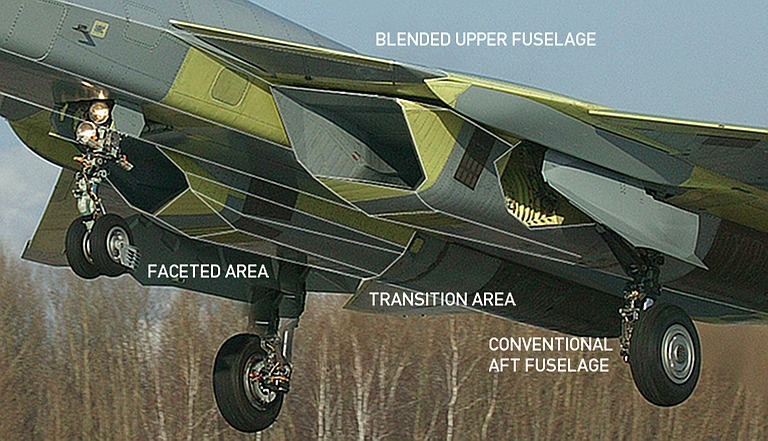
The F-22’s design incorporates several features that contribute to its low RCS. These include:
- Curved surfaces: The F-22's airframe is designed with curved surfaces that help to scatter radar waves in different directions, reducing the amount of energy that is reflected back to the radar antenna.
- Serrated edges: The edges of the F-22's wings and control surfaces are serrated, which helps to reduce the amount of radar energy that is reflected back to the radar antenna.
- Radar-absorbing materials (RAMs): The F-22's airframe is treated with RAMs, which are designed to absorb radar energy rather than reflecting it back to the radar antenna.
Evasion Tactics
In addition to its low RCS, the F-22 is also equipped with advanced evasion tactics that allow it to avoid detection and engagement by enemy air defenses. These tactics include:
- Low-observable flight profiles: The F-22 can fly low-observable flight profiles, which involve flying at low altitudes and using terrain to mask its radar signature.
- Electronic countermeasures (ECMs): The F-22 is equipped with advanced ECMs, which can detect and disrupt enemy radar systems, making it harder for them to detect and track the aircraft.
- Network-centric warfare: The F-22 can share data with other aircraft and ground stations in real-time, allowing it to stay informed about the location and status of enemy air defenses and adjust its tactics accordingly.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Curved surfaces | Help to scatter radar waves in different directions |
| Serrated edges | Reduce the amount of radar energy reflected back to the radar antenna |
| Radar-absorbing materials (RAMs) | Absorb radar energy rather than reflecting it back to the radar antenna |

The F-22's low RCS and advanced evasion tactics have been demonstrated in several exercises and operations, where the aircraft has consistently shown its ability to penetrate hostile airspace undetected. The exact details of these exercises and operations are classified, but they have helped to validate the F-22's stealth capabilities and demonstrate its effectiveness as a frontline fighter jet.
Technical Specifications
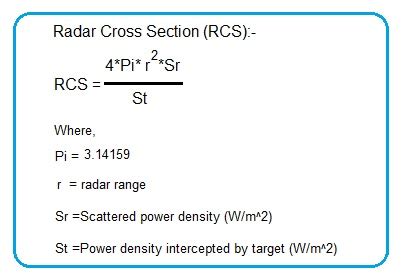
The F-22’s technical specifications are a key factor in its low RCS and advanced evasion tactics. Some of the key specifications include:
- Length: 62.1 feet (18.9 meters)
- Wingspan: 44.6 feet (13.6 meters)
- Height: 16.7 feet (5.1 meters)
- Empty weight: 43,430 pounds (19,700 kilograms)
- Maximum takeoff weight: 80,000 pounds (36,300 kilograms)
- Engines: 2 x Pratt & Whitney F119-PW-100 turbofans, each producing 35,000 pounds of thrust
The F-22's advanced avionics and sensor systems also play a critical role in its evasion tactics. These systems include:
- AN/APG-77 radar: A high-resolution, active electronically scanned array (AESA) radar system that provides advanced air-to-air and air-to-ground capabilities.
- AN/ALR-94 radar warning receiver: A system that detects and analyzes enemy radar emissions, providing the F-22 with real-time information about the location and status of enemy air defenses.
- AN/AAR-56 infrared search and track system: A system that detects and tracks enemy aircraft using infrared sensors, providing the F-22 with a passive detection capability.
What is the F-22's radar cross-section (RCS)?
+The exact RCS of the F-22 is classified, but it is widely reported to be less than 0.01 square meters.
What design features contribute to the F-22's low RCS?
+The F-22's curved surfaces, serrated edges, and radar-absorbing materials (RAMs) all contribute to its low RCS.
What evasion tactics does the F-22 use to avoid detection and engagement by enemy air defenses?
+The F-22 uses low-observable flight profiles, electronic countermeasures (ECMs), and network-centric warfare to avoid detection and engagement by enemy air defenses.
In conclusion, the F-22’s low RCS and advanced evasion tactics make it an extremely difficult target to detect and engage, giving it a significant advantage in combat scenarios. The aircraft’s design features, including its curved surfaces, serrated edges, and RAMs, all contribute to its low RCS, while its advanced avionics and sensor systems provide it with the capability to detect and analyze enemy radar emissions, and to share data with other aircraft and ground stations in real-time.


