Glycolysis Reaction Guide Pdf
Glycolysis is a fundamental metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate, releasing energy and forming ATP and NADH in the process. This reaction is crucial for the survival of nearly all living organisms, from bacteria to humans. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of glycolysis, exploring its reactants, products, enzymes, and regulation, as well as its significance in various biological contexts.
Introduction to Glycolysis

Glycolysis is a multi-step biochemical pathway that occurs in the cytosol of cells. It is the first step in cellular respiration, where glucose, a six-carbon sugar, is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate, a three-carbon compound. This process releases a small amount of energy, which is captured in the form of ATP and NADH. Glycolysis is an essential reaction for generating energy, especially under anaerobic conditions, where oxygen is absent.
Glycolytic Pathway
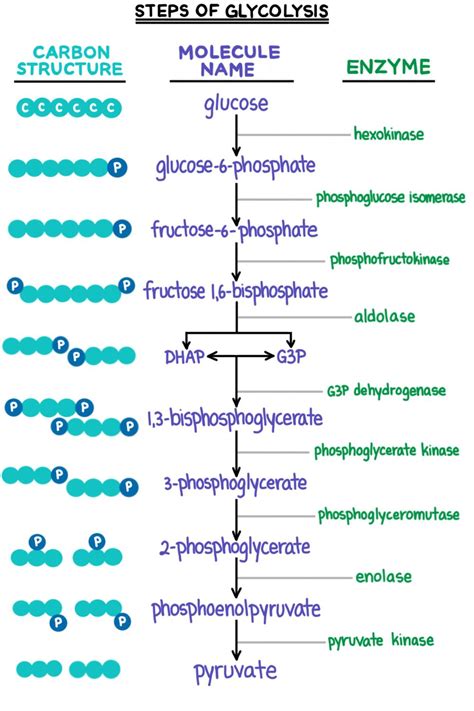
The glycolytic pathway consists of ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions, each with its own unique characteristics and importance. The pathway can be divided into two phases: the investment phase, where ATP is consumed to convert glucose into fructose-1,6-bisphosphate, and the payoff phase, where ATP and NADH are produced from the conversion of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate into pyruvate.
| Reaction | Enzyme | Reactants | Products |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hexokinase | Glucose + ATP | Glucose-6-phosphate + ADP |
| 2 | Phosphoglucose Isomerase | Glucose-6-phosphate | Fructose-6-phosphate |
| 3 | Phosphofructokinase-1 | Fructose-6-phosphate + ATP | Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate + ADP |
| 4 | Aldolase | Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate + Dihydroxyacetone phosphate |
| 5 | Triosephosphate Isomerase | Dihydroxyacetone phosphate | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate |
| 6 | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate Dehydrogenase | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate + NAD+ + Pi | 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate + NADH + H+ |
| 7 | Phosphoglycerate Kinase | 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate + ADP | 3-Phosphoglycerate + ATP |
| 8 | Phosphoglycerate Mutase | 3-Phosphoglycerate | 2-Phosphoglycerate |
| 9 | Enolase | 2-Phosphoglycerate | Enolpyruvate |
| 10 | Pyruvate Kinase | Enolpyruvate + ADP + H+ | Pyruvate + ATP |

Regulation of Glycolysis

Glycolysis is a highly regulated pathway, with multiple mechanisms in place to ensure that it operates efficiently and effectively. The regulation of glycolysis involves the coordinated action of various enzymes, metabolites, and signaling pathways. Key regulatory mechanisms include feedback inhibition, allosteric control, and covalent modification of enzymes.
Feedback Inhibition
Feedback inhibition is a critical mechanism for regulating glycolysis. When the concentration of ATP is high, it binds to and inhibits the activity of phosphofructokinase-1, thereby reducing the flux through the glycolytic pathway. Conversely, when the concentration of ADP is high, it activates phosphofructokinase-1, increasing the flux through the pathway.
Allosteric Control
Allosteric control is another important mechanism for regulating glycolysis. Enzymes such as hexokinase, phosphofructokinase-1, and pyruvate kinase are allosterically controlled by various metabolites, including ATP, ADP, and citrate. These metabolites bind to specific sites on the enzymes, either activating or inhibiting their activity.
What is the primary function of glycolysis?
+The primary function of glycolysis is to convert glucose into pyruvate, releasing energy and forming ATP and NADH in the process.
What are the key regulatory enzymes in glycolysis?
+The key regulatory enzymes in glycolysis include hexokinase, phosphofructokinase-1, and pyruvate kinase.
What is the significance of glycolysis in various biological contexts?
+Glycolysis is essential for generating energy, especially under anaerobic conditions. It also plays a critical role in various biological processes, including cell growth, differentiation, and survival.
Significance of Glycolysis

Glycolysis is a vital metabolic pathway that plays a critical role in various biological contexts. It is essential for generating energy, especially under anaerobic conditions, and is also involved in various cellular processes, including cell growth, differentiation, and survival.
Energy Production
Glycolysis is a primary source of energy for cells, especially under anaerobic conditions. It produces a small amount of energy in the form of ATP and NADH, which can be used to fuel various cellular processes.
Cellular Processes
Glycolysis is also involved in various cellular processes, including cell growth, differentiation, and survival. It provides the necessary energy and building blocks for the synthesis of biomolecules, such as amino acids, nucleotides, and lipids.
In conclusion, glycolysis is a complex and highly regulated metabolic pathway that plays a critical role in various biological contexts. Its significance extends beyond energy production, as it is also involved in various cellular processes, including cell growth, differentiation, and survival. Understanding the mechanisms of glycolysis and its regulation is essential for appreciating its importance in maintaining cellular homeostasis and for developing therapeutic strategies to treat various diseases.



