Ct Guided Biopsy
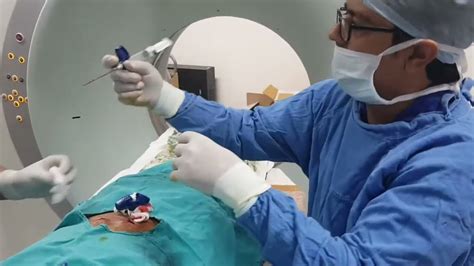
Computed Tomography (CT) guided biopsy is a medical procedure that uses CT scans to guide the insertion of a needle into a suspected tumor or abnormal tissue to collect a sample for further examination. This procedure is commonly used to diagnose various types of cancer, including lung, liver, kidney, and bone cancer. The use of CT guidance allows for precise targeting of the lesion, reducing the risk of complications and improving the accuracy of the biopsy results.
Indications and Contraindications

CT guided biopsy is typically indicated for patients with a suspected tumor or abnormal tissue that cannot be easily accessed through a traditional surgical biopsy. This may include lesions that are deep within the body, small in size, or located in a sensitive area. The procedure is also used to collect tissue samples from patients who have undergone previous surgeries or have a high risk of complications from a traditional biopsy. However, there are certain contraindications to consider, including patients with severe bleeding disorders, those who are taking anticoagulant medications, and women who are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Pre-Procedural Preparation
Before undergoing a CT guided biopsy, patients are typically required to undergo a series of tests to ensure they are suitable for the procedure. These tests may include blood work to check for bleeding disorders, a physical examination to assess overall health, and a review of medical history to identify any potential risks. Patients are also advised to avoid eating or drinking for several hours before the procedure and to wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing. In some cases, patients may be required to undergo a CT scan before the biopsy to confirm the location and size of the lesion.
| Pre-Procedural Test | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Blood work | To check for bleeding disorders |
| Physical examination | To assess overall health |
| Medical history review | To identify potential risks |
| CT scan | To confirm lesion location and size |

Procedure Overview

The CT guided biopsy procedure typically takes place in a radiology department and is performed by a team of medical professionals, including a radiologist, nurse, and technologist. The patient is positioned on a CT table, and a local anesthetic is administered to numb the area where the needle will be inserted. The radiologist then uses the CT scanner to guide the needle into the lesion, taking care to avoid any surrounding structures or organs. Once the needle is in place, a tissue sample is collected and sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Types of Biopsy Needles
There are several types of biopsy needles that can be used during a CT guided biopsy, including fine-needle aspiration (FNA) needles, core needles, and vacuum-assisted biopsy needles. FNA needles are the smallest and are used to collect a small sample of cells, while core needles are larger and are used to collect a larger tissue sample. Vacuum-assisted biopsy needles use a vacuum device to collect multiple samples from a single insertion site.
- Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) needles: used to collect small cell samples
- Core needles: used to collect larger tissue samples
- Vacuum-assisted biopsy needles: used to collect multiple samples from a single site
Post-Procedural Care

After the CT guided biopsy procedure, patients are typically monitored for several hours to check for any signs of bleeding or complications. Patients may experience some discomfort or pain at the biopsy site, which can be managed with pain medication. It is essential for patients to follow their doctor’s instructions regarding post-procedural care, including avoiding strenuous activities and taking medications as directed. The results of the biopsy are typically available within a few days, and patients will need to follow up with their doctor to discuss the results and any further treatment options.
Complications and Risks
As with any medical procedure, there are potential complications and risks associated with CT guided biopsy. These may include bleeding, infection, and damage to surrounding structures or organs. Patients should be aware of the potential risks and discuss any concerns with their doctor before undergoing the procedure.
What are the benefits of CT guided biopsy?
+The benefits of CT guided biopsy include precise targeting of the lesion, reduced risk of complications, and improved accuracy of biopsy results. The procedure is also less invasive than traditional surgical biopsies and can be performed on an outpatient basis.
How long does the CT guided biopsy procedure take?
+The CT guided biopsy procedure typically takes between 30 minutes to several hours, depending on the complexity of the procedure and the number of samples collected.
What are the potential complications of CT guided biopsy?
+Potential complications of CT guided biopsy include bleeding, infection, and damage to surrounding structures or organs. Patients should discuss any concerns with their doctor before undergoing the procedure.



