Air Guard Vs Army Guard: Compare Benefits & Careers

The Air National Guard (Air Guard) and the Army National Guard (Army Guard) are two distinct branches of the National Guard, each offering unique benefits and career opportunities. While both branches share the common goal of supporting national defense and responding to domestic emergencies, they have different missions, requirements, and cultures. In this article, we will delve into the specifics of each branch, comparing their benefits, careers, and requirements to help individuals make informed decisions about their military service.
Overview of the Air National Guard and Army National Guard

The Air National Guard is a reserve component of the United States Air Force, with a primary mission of providing air power support to the Active Duty Air Force. The Army National Guard, on the other hand, is a reserve component of the United States Army, with a primary mission of providing ground troops to support Army operations. Both branches have a dual mission, supporting both federal and state authorities in times of need.
Mission and Culture
The Air Guard’s mission is focused on air power, with an emphasis on flying operations, aircraft maintenance, and supporting the Air Force’s global operations. The Army Guard’s mission is focused on ground operations, with an emphasis on infantry, artillery, and engineer units. The culture of the Air Guard tends to be more formal and structured, reflecting the Air Force’s traditions and values. In contrast, the Army Guard’s culture is often more flexible and adaptable, reflecting the Army’s emphasis on mission accomplishment and teamwork.
| Branch | Mission | Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Air National Guard | Air power support | Formal, structured |
| Army National Guard | Ground operations | Flexible, adaptable |
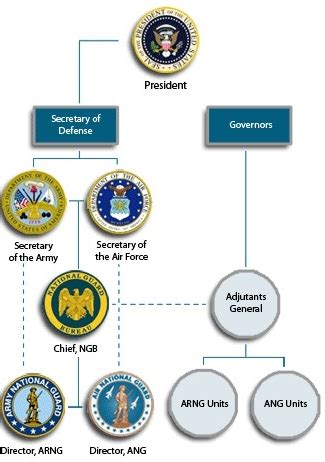
Benefits Comparison

Both the Air Guard and Army Guard offer a range of benefits, including education assistance, healthcare, and retirement plans. However, there are some key differences between the two branches. The Air Guard offers more comprehensive education benefits, including the Air National Guard’s Post-9⁄11 GI Bill and the Tuition Assistance Program. The Army Guard, on the other hand, offers more flexible deployment options and a wider range of military occupational specialties (MOS).
Education Benefits
The Air Guard’s education benefits include up to 100% tuition coverage for undergraduate and graduate degree programs, as well as vocational training and certification programs. The Army Guard’s education benefits include up to 100% tuition coverage for undergraduate degree programs, as well as vocational training and certification programs. However, the Army Guard’s benefits may vary depending on the state and the individual’s MOS.
| Branch | Education Benefits |
|---|---|
| Air National Guard | Up to 100% tuition coverage for undergraduate and graduate degree programs |
| Army National Guard | Up to 100% tuition coverage for undergraduate degree programs |
Career Opportunities

Both the Air Guard and Army Guard offer a wide range of career opportunities, from enlisted roles to officer positions. The Air Guard has a strong focus on aviation careers, including pilots, navigators, and aircraft maintenance specialists. The Army Guard, on the other hand, has a strong focus on infantry and combat arms careers, including infantrymen, artillerymen, and engineers.
Enlisted Careers
The Air Guard offers over 200 enlisted career fields, including aviation, logistics, and communications. The Army Guard offers over 150 enlisted career fields, including infantry, artillery, and engineer units. Both branches offer opportunities for advancement and professional development, including non-commissioned officer (NCO) and warrant officer positions.
- Air Guard enlisted careers: aviation, logistics, communications
- Army Guard enlisted careers: infantry, artillery, engineer units
Requirements and Eligibility

To join the Air Guard or Army Guard, individuals must meet specific eligibility requirements, including age, education, and physical fitness standards. The Air Guard requires a minimum ASVAB score of 31, while the Army Guard requires a minimum ASVAB score of 31 for some MOS. Both branches require a high school diploma or equivalent and a background check.
Physical Fitness Standards
The Air Guard and Army Guard have different physical fitness standards, reflecting their unique mission requirements. The Air Guard requires a minimum 1.5-mile run time of 16:30 minutes, while the Army Guard requires a minimum 2-mile run time of 15:00 minutes. Both branches require a body mass index (BMI) within a healthy range and a medical screening prior to enlistment.
| Branch | Physical Fitness Standards |
|---|---|
| Air National Guard | 1.5-mile run time: 16:30 minutes |
| Army National Guard | 2-mile run time: 15:00 minutes |
What are the main differences between the Air Guard and Army Guard?
+The main differences between the Air Guard and Army Guard are their mission, culture, and career opportunities. The Air Guard is focused on air power, while the Army Guard is focused on ground operations. The Air Guard has a more formal and structured culture, while the Army Guard is more flexible and adaptable.
What are the education benefits of joining the Air Guard or Army Guard?
+Both the Air Guard and Army Guard offer comprehensive education benefits, including tuition assistance and vocational training. The Air Guard offers up to 100% tuition coverage for undergraduate and graduate degree programs, while the Army Guard offers up to 100% tuition coverage for undergraduate degree programs.
What are the career opportunities available in the Air Guard and Army Guard?
+Both the Air Guard and Army Guard offer a wide range of career opportunities, from enlisted roles to officer positions. The Air Guard has a strong focus on aviation careers, while the Army Guard has a strong focus on infantry and combat arms careers. Both branches offer opportunities for advancement and professional development.
