10+ Us Deployment Strategies That Work Today
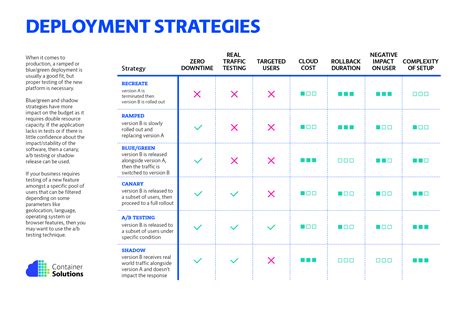
The United States (US) deployment strategies have evolved significantly over the years, with a focus on achieving operational success while minimizing risks and costs. Today, various deployment strategies are employed by the US military, each with its unique characteristics and advantages. In this article, we will explore 10+ US deployment strategies that work today, highlighting their key features, benefits, and examples.
Introduction to US Deployment Strategies

The US military employs a range of deployment strategies to achieve its operational objectives, from combat operations to humanitarian assistance and disaster response. These strategies are designed to optimize the use of resources, minimize risks, and maximize effectiveness. The US deployment strategies can be broadly categorized into several types, including expeditionary operations, rotational deployments, permanent basing, and hybrid approaches. Each of these strategies has its strengths and weaknesses, and the choice of strategy depends on the specific operational context and requirements.
Expeditionary Operations
Expeditionary operations involve the deployment of military forces to a remote or austere location, often with limited infrastructure and support. This strategy is commonly used for combat operations, humanitarian assistance, and disaster response. The US military has developed a range of expeditionary capabilities, including amphibious assault ships, expeditionary airfields, and mobile command centers. These capabilities enable the US military to rapidly deploy and operate in a variety of environments, from desert to jungle to urban areas.
| Expeditionary Operation | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Amphibious Assault | Rapid deployment, flexible operational capability |
| Expeditionary Airfield | Temporary airbase, expeditionary logistics |
| Mobile Command Center | Decentralized command, real-time situational awareness |

Rotational Deployments

Rotational deployments involve the rotation of military units into and out of a theater of operation, often on a regular schedule. This strategy is commonly used for peacekeeping operations, security cooperation, and training exercises. The US military has developed a range of rotational deployment models, including unit rotations, individual augmentations, and training rotations. These models enable the US military to maintain a consistent operational presence while minimizing the risks and costs associated with long-term deployments.
Permanent Basing
Permanent basing involves the establishment of a permanent military base or presence in a foreign country or region. This strategy is commonly used for strategic deterrence, security cooperation, and logistics support. The US military has developed a range of permanent basing models, including main operating bases, forward operating bases, and cooperative security locations. These models enable the US military to maintain a persistent operational presence while minimizing the risks and costs associated with rotational deployments.
| Permanent Basing Model | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Main Operating Base | Permanent infrastructure, strategic logistics |
| Forward Operating Base | Temporary infrastructure, tactical logistics |
| Cooperative Security Location | Shared infrastructure, cooperative security |
Hybrid Approaches
Hybrid approaches involve the combination of different deployment strategies to achieve operational objectives. This strategy is commonly used for complex operations, multinational operations, and irregular warfare. The US military has developed a range of hybrid approaches, including expeditionary-rotational hybrids, permanent-rotational hybrids, and network-centric hybrids. These approaches enable the US military to optimize the use of resources, minimize risks, and maximize effectiveness in a variety of operational contexts.
Network-Centric Hybrids
Network-centric hybrids involve the use of networked systems and capabilities to enable expeditionary operations, rotational deployments, and permanent basing. This approach is commonly used for command and control, intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance, and logistics support. The US military has developed a range of network-centric capabilities, including satellite communications, cybersecurity, and cloud computing. These capabilities enable the US military to maintain a persistent operational presence, project power across the globe, and optimize the use of resources.
| Network-Centric Capability | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Satellite Communications | Global connectivity, secure communications |
| Cybersecurity | Network defense, threat detection |
| Cloud Computing | Scalable infrastructure, on-demand services |
Other US Deployment Strategies

In addition to the strategies mentioned above, the US military employs a range of other deployment strategies, including airborne operations, special operations, and humanitarian assistance. These strategies are designed to achieve specific operational objectives, from rapid deployment to long-term engagement. The US military has developed a range of capabilities to support these strategies, including airlift, sealift, and logistics support.
Airborne Operations
Airborne operations involve the use of aircraft to deploy military forces, equipment, and supplies. This strategy is commonly used for rapid deployment, emergency response, and humanitarian assistance. The US military has developed a range of airborne capabilities, including transport aircraft, helicopters, and airborne command centers. These capabilities enable the US military to rapidly deploy and operate in a variety of environments, from desert to jungle to urban areas.
| Airborne Capability | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Transport Aircraft | Rapid deployment, heavy lift |
| Helicopters | Vertical takeoff, tactical logistics |
| Airborne Command Center | Decentralized command, real-time situational awareness |
What are the key features of US deployment strategies?
+The key features of US deployment strategies include expeditionary operations, rotational deployments, permanent basing, and hybrid approaches. These strategies are designed to optimize the use of resources, minimize risks, and maximize effectiveness in a variety of operational contexts.
What are the benefits of US deployment strategies?
+The benefits of US deployment strategies include rapid deployment, flexible operational capability, and persistent operational presence. These benefits enable the US military to project power across the globe, maintain a consistent operational capability, and



