10 Tropical Cyclone Nine Facts You Need To Know

Tropical cyclones are powerful and fascinating weather phenomena that capture the attention of meteorologists and the public alike. As we delve into the intricacies of Tropical Cyclone Nine, we uncover a wealth of knowledge that sheds light on the intricacies of these formidable storms. In this article, we present 10 essential facts that will enhance your understanding of these awe-inspiring natural occurrences.
1. Formation and Origins
Tropical Cyclone Nine, like all tropical cyclones, originates from specific atmospheric conditions. It typically forms over warm ocean waters, where the sea surface temperature is at least 26.5°C (80°F). The warm, moist air rises, creating low-pressure zones that draw in surrounding air, leading to the development of the cyclone’s distinctive spiral structure.
Key Atmospheric Factors
- Warm ocean temperatures
- Moisture-laden air
- Low-pressure systems
- Rotation due to the Coriolis effect
Regional Variations
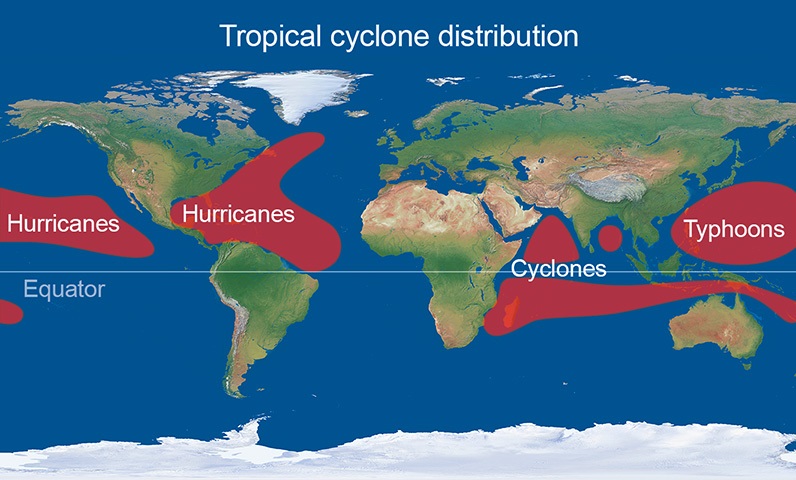
While the basic formation process is similar, tropical cyclones are given different names based on their location. For instance, in the Atlantic and Northeast Pacific, they are called hurricanes, while in the Northwest Pacific, they are known as typhoons. In the Indian Ocean and Southwest Pacific, the term “cyclone” is used.
2. Intensity and Classification

Tropical Cyclone Nine’s intensity is categorized using various classification systems, with the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale being one of the most widely recognized. This scale categorizes hurricanes into five categories based on their sustained wind speeds.
| Category | Sustained Wind Speed (mph) |
|---|---|
| Category 1 | 74-95 |
| Category 2 | 96-110 |
| Category 3 (Major Hurricane) | 111-129 |
| Category 4 (Major Hurricane) | 130-156 |
| Category 5 (Major Hurricane) | 157 and higher |
Impact and Hazards
The intensity of a tropical cyclone directly influences its impact on coastal regions. Strong winds, heavy rainfall, storm surges, and flooding are some of the primary hazards associated with these storms. The potential for significant damage and loss of life increases with higher category cyclones.
3. Tracking and Forecasting
Advancements in technology have revolutionized the tracking and forecasting of tropical cyclones. Meteorologists utilize a combination of satellite imagery, radar systems, and ground-based observations to monitor the storm’s path and intensity.
Key Tools and Techniques
- Satellite Imagery: Provides real-time visual data on the cyclone’s structure and movement.
- Doppler Radar: Measures wind speed and direction, aiding in the prediction of potential hazards.
- Buoys and Drifting Probes: Deployed in the ocean to collect data on water temperature and wind patterns.
- Hurricane Hunter Aircraft: Specially equipped planes fly into the storm to gather critical data.
Challenges in Forecasting
Despite these advancements, forecasting tropical cyclones remains a complex task. Factors like rapid intensification, unpredictable movement, and the impact of atmospheric conditions can pose challenges, making accurate predictions a continuous area of research and improvement.
4. Storm Structure and Anatomy
The structure of Tropical Cyclone Nine is a marvel of nature, with distinct components contributing to its overall power.
Eye and Eyewall
At the center of the cyclone lies the eye, a relatively calm region with light winds and fair weather. Surrounding the eye is the eyewall, a ring of intense thunderstorms where the strongest winds and heaviest rainfall occur.
Rainbands and Spiral Bands
Outside the eyewall, spiral bands of thunderstorms extend outward, often in a spiral pattern. These bands can produce heavy rainfall and strong winds, sometimes causing significant damage to coastal areas.
Inner Core and Outer Core
The inner core of the cyclone, including the eye and eyewall, is where the most intense weather conditions are found. The outer core, on the other hand, consists of less organized weather systems that can still bring heavy rainfall and high winds.
5. Impact on Marine Life
Tropical cyclones have a significant impact on marine ecosystems. While they can cause harm to certain species, they also play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of marine life.
Positive Effects
- Nutrient Upwelling: Strong winds and waves stir up nutrients from deeper waters, benefiting phytoplankton and the entire marine food chain.
- Spawning and Reproduction: Some fish and marine species use the stormy conditions to trigger spawning events, ensuring the survival of their offspring.
- Habitat Creation: Tropical cyclones can create new habitats by reshaping coastlines and depositing sediment, providing shelter for various marine organisms.
Negative Effects
- Destruction of Coral Reefs: High winds and storm surges can damage coral reefs, leading to the loss of critical marine habitats.
- Fish Kills: Rapid changes in water temperature and oxygen levels can be detrimental to fish populations.
- Displacement of Marine Life: Strong currents and waves can displace marine organisms, disrupting their natural migration patterns.
6. Economic Impact and Preparedness
The economic impact of Tropical Cyclone Nine can be significant, affecting various sectors and industries. Preparedness and resilience are crucial to mitigating these effects.
Agriculture and Food Security
Tropical cyclones can damage crops, livestock, and agricultural infrastructure, leading to food shortages and economic losses. Implementing resilient agricultural practices and early warning systems can help minimize these impacts.
Infrastructure and Construction
The destruction of buildings, roads, and critical infrastructure is a common consequence of tropical cyclones. Adhering to strict building codes and designing resilient infrastructure can reduce the economic burden of rebuilding.
Tourism and Recreation
Tropical cyclones can disrupt tourism activities, affecting local economies. By implementing effective communication and evacuation plans, tourist destinations can minimize the impact and ensure the safety of visitors.
7. Historical Significance
Tropical Cyclone Nine is part of a long history of powerful storms that have shaped our understanding of meteorology and impacted human civilization.
Notable Historical Cyclones
- Hurricane Katrina (2005): Caused catastrophic damage along the Gulf Coast of the United States, leading to significant policy changes in disaster preparedness and response.
- Super Typhoon Haiyan (2013): One of the strongest tropical cyclones ever recorded, it devastated the Philippines, highlighting the need for improved early warning systems and international aid.
- Hurricane Andrew (1992): A Category 5 hurricane that caused extensive damage in South Florida, leading to significant advancements in building codes and hurricane forecasting.
Lessons Learned
The study of historical cyclones provides valuable insights into the long-term effects of these storms, guiding researchers and policymakers in developing more resilient communities and infrastructure.
8. Environmental Impacts
Beyond the immediate impacts on human life and infrastructure, tropical cyclones also have significant environmental consequences.
Erosion and Sediment Transport
Strong winds and waves associated with tropical cyclones can lead to coastal erosion, reshaping shorelines and depositing sediment in new locations. This process can impact ecosystems and infrastructure along the coast.
Saltwater Intrusion
Tropical cyclones can cause saltwater intrusion into freshwater aquifers, affecting drinking water supplies and agricultural irrigation. Proper management of water resources is crucial to mitigate these impacts.
Air Quality
The intense winds and heavy rainfall can stir up dust and pollutants, leading to temporary decreases in air quality. Monitoring and mitigating these effects are essential for public health and environmental protection.
9. Tropical Cyclone Nine and Climate Change
The relationship between tropical cyclones and climate change is a topic of ongoing research and debate.
Potential Effects of Climate Change
- Increased Intensity: Warmer ocean temperatures due to climate change may lead to more intense tropical cyclones with higher wind speeds and rainfall.
- Changing Patterns: Shifts in atmospheric circulation patterns could alter the frequency and distribution of tropical cyclones, affecting vulnerable regions.
- Rapid Intensification: Some studies suggest that climate change may contribute to more rapid intensification of tropical cyclones, making forecasting even more challenging.
Adaptation and Resilience
Understanding the potential impacts of climate change on tropical cyclones is crucial for developing effective adaptation strategies. This includes improving early warning systems, enhancing infrastructure resilience, and promoting sustainable land use practices.
10. Community Resilience and Preparedness
Building community resilience is essential for minimizing the impacts of Tropical Cyclone Nine and other natural disasters.
Education and Awareness
Educating communities about the risks and hazards associated with tropical cyclones is crucial. Providing accurate and timely information can help individuals make informed decisions and take appropriate actions during a storm.
Evacuation Plans and Shelters
Developing comprehensive evacuation plans and ensuring the availability of well-equipped shelters are vital components of community preparedness. These measures can save lives and reduce the overall impact of the storm.
Post-Storm Recovery and Rebuilding
Effective post-storm recovery efforts, including debris removal, infrastructure repair, and community support, are essential for long-term resilience. A coordinated response can help communities rebuild stronger and more prepared for future storms.
How can I stay safe during a tropical cyclone?
+During a tropical cyclone, it’s crucial to stay informed and follow official instructions. Here are some key safety measures:
- Heed evacuation orders and seek shelter in designated evacuation centers or with family/friends in safer areas.
- Secure your home by boarding up windows, bringing in outdoor items, and ensuring a supply of food and water.
- Stay indoors and away from windows during the storm.
- Monitor official sources for updates and follow any specific instructions for your area.
- Be prepared for potential power outages and have a backup plan for communication and lighting.
What are the key differences between a hurricane, typhoon, and cyclone?
+These terms refer to the same weather phenomenon but are used in different regions:
- Hurricane: Used in the Atlantic and Northeast Pacific.
- Typhoon: Used in the Northwest Pacific.
- Cyclone: Used in the Indian Ocean and Southwest Pacific.
How do tropical cyclones impact wildlife and ecosystems?
+Tropical cyclones can have both positive and negative impacts on wildlife and ecosystems. While they can cause harm to certain species, they also play a role in maintaining the balance of marine life through nutrient upwelling, spawning events, and habitat creation. However, strong winds and storm surges can also damage coral reefs and disrupt marine migration patterns.