10 Ford Aircraft Carrier Advantages
The Ford-class aircraft carriers, led by the USS Gerald R. Ford (CVN-78), represent a significant leap forward in naval aviation technology and capability. These carriers are designed to provide the United States Navy with a robust and flexible platform for power projection and deterrence, offering numerous advantages over their predecessors. Here, we'll explore ten key advantages of the Ford-class aircraft carriers, highlighting their innovative design, advanced technologies, and enhanced operational capabilities.
Introduction to the Ford-Class Advantages

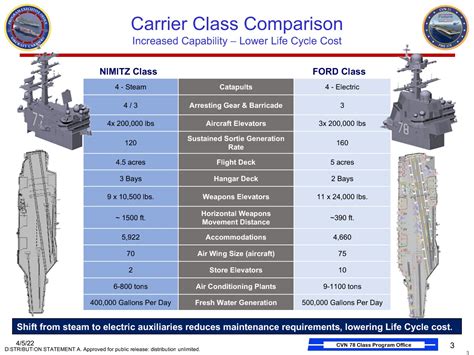
The development of the Ford-class aircraft carriers was driven by the need to replace the aging Nimitz-class carriers, which have been the backbone of the U.S. Navy’s fleet since the 1970s. The Ford class incorporates a range of new technologies and design features aimed at improving efficiency, reducing operating costs, and enhancing the carriers’ ability to support a wide range of military operations. From advanced propulsion systems to enhanced aircraft handling and launch capabilities, these carriers embody the latest in naval aviation technology.
Advantage 1: Electromagnetic Aircraft Launch System (EMALS)
One of the most significant innovations of the Ford-class carriers is the Electromagnetic Aircraft Launch System (EMALS). EMALS replaces the traditional steam catapults used on earlier carriers, offering a more efficient, reliable, and safer means of launching aircraft. EMALS can launch a wider range of aircraft, from small unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) to heavy strike fighters, with less stress on the airframes and less maintenance required for the launch system itself. This capability enhances the flexibility and operational readiness of the carrier’s air wing.
Advantage 2: Advanced Arresting Gear (AAG)
Complementing EMALS is the Advanced Arresting Gear (AAG), designed to bring aircraft to a safe stop after landing. The AAG system uses water-cooled induction motors to generate the arresting force, providing a more consistent and controlled arrest. This system is capable of handling a broader range of aircraft weights and speeds, improving safety and reducing the wear and tear on aircraft and the arresting gear itself. The AAG is more reliable and requires less maintenance than traditional arresting systems, further enhancing the carrier’s operational efficiency.
Advantage 3: Dual-Band Radar (DBR)
The Ford-class carriers are equipped with a Dual-Band Radar (DBR) system, which integrates X-band and S-band radar capabilities. This advanced radar system provides improved air and missile defense capabilities, enhanced situational awareness, and supports the launch and recovery of aircraft. The DBR offers better performance in adverse weather conditions and against low-observable targets, significantly enhancing the carrier’s self-defense and air defense capabilities.
Advantage 4: Increased Electrical Power Generation
The Ford-class design includes a new nuclear reactor design, the A4W reactor, which provides 25% more electrical power than the reactors on Nimitz-class carriers. This increased power generation capacity supports the operation of advanced systems like EMALS and AAG, as well as future technologies that may be integrated into the carrier. The additional power also allows for more efficient operation of onboard systems, reducing the carrier’s operational costs and environmental impact.
Advantage 5: Reduced Crew Requirements
Through the use of advanced automation and streamlined design, the Ford-class carriers require significantly fewer personnel to operate than their predecessors. This reduction in crew size decreases operational costs and enhances the quality of life for sailors, as fewer personnel are needed to maintain and operate the ship. Automated systems for tasks such as aircraft handling, cargo movement, and maintenance reduce the workload on the crew, allowing for a more focused and effective deployment of personnel.
Advantage 6: Enhanced Aircraft Elevators
The Ford-class carriers feature advanced aircraft elevators that are faster, more reliable, and require less maintenance than those on earlier carriers. These elevators use advanced electromechanical systems to move aircraft between the flight deck and the hangar bay more efficiently, reducing the time required to prepare aircraft for launch and recovery. This enhancement in aircraft elevator performance supports a higher operational tempo for the carrier’s air wing.
Advantage 7: Improved Propulsion Efficiency
The new reduced-maintenance propulsion system on the Ford-class carriers offers improved efficiency and reliability. The main reduction gear and other components are designed to require less maintenance, reducing downtime and supporting longer periods at sea without the need for major repairs. This propulsion system, combined with the more efficient nuclear reactor, contributes to the overall reduced operating cost of the Ford-class carriers.
Advantage 8: Advanced Combat Systems
The Ford-class carriers are equipped with advanced combat systems that provide enhanced situational awareness, command and control, and weapon systems integration. These systems support more effective air and missile defense, anti-submarine warfare, and surface warfare capabilities, making the Ford-class carriers highly formidable platforms for power projection and deterrence.
Advantage 9: Enhanced Survivability
The design of the Ford-class carriers incorporates numerous features aimed at enhancing their survivability in combat. These include redundant systems for critical functions, advanced damage control systems, and a reduced radar cross-section design to decrease the carrier’s visibility to enemy radar. These features improve the carrier’s ability to withstand and recover from damage, ensuring that it can continue to operate effectively in hostile environments.
Advantage 10: Future Proofing and Flexibility
Finally, the Ford-class carriers are designed with future-proofing in mind, incorporating modular design principles and flexible infrastructure to accommodate the integration of new technologies and systems as they become available. This flexibility enables the carriers to adapt to evolving operational requirements and technological advancements, ensuring that they remain relevant and effective throughout their service lives.
| System/Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| EMALS | Electromagnetic Aircraft Launch System for more efficient and safer launches |
| AAG | Advanced Arresting Gear for controlled and consistent aircraft recovery |
| DBR | Dual-Band Radar for enhanced air and missile defense |
| A4W Reactor | Increased electrical power generation for advanced systems |
| Reduced Crew | Streamlined operations and automation reduce personnel requirements |
| Advanced Elevators | Faster and more reliable aircraft movement between decks |
| Propulsion Efficiency | Improved propulsion system reliability and efficiency |
| Combat Systems | Advanced command, control, and weapon systems integration |
| Survivability Features | Enhanced design for survivability, including redundant systems and reduced radar cross-section |
| Future Proofing | Modular design for easy integration of future technologies |

What is the primary advantage of the Electromagnetic Aircraft Launch System (EMALS) on Ford-class carriers?
+The primary advantage of EMALS is its ability to launch aircraft more efficiently and safely, with less stress on airframes and reduced maintenance requirements compared to traditional steam catapults.
How does the Advanced Arresting Gear (AAG) system enhance aircraft recovery on Ford-class carriers?
+The AAG system provides a more consistent and controlled arrest, capable of handling a broader range of aircraft weights and speeds, improving safety and reducing wear and tear on both aircraft and the arresting gear.
What role do Ford-class carriers play in supporting national defense strategies?
+Ford-class carriers serve as pivotal assets for power projection and deterrence, providing a flexible and robust platform for a wide range of military operations. Their advanced technologies and design features enable them to support various missions, from air and missile defense to surface